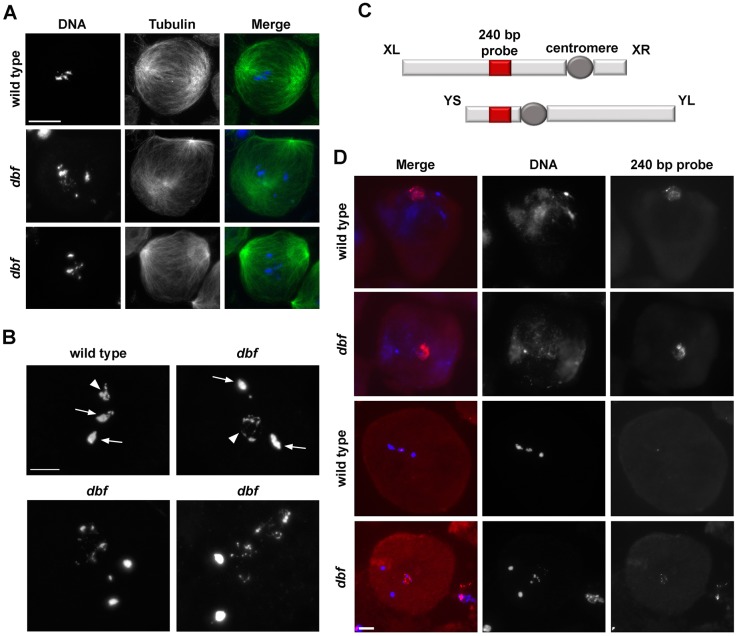
Fig. 2.
Doublefault is required for sex chromosome condensation in male meiotic cells. (A) Wild-type and dbf z3318/Df(2L)Exel802 (dbf) mutant spermatocytes in prometaphase (stage M2) stained for α-tubulin (green) and DNA (blue). (B) Metaphase chromosomes from wild-type and dbf z3318/Df(2L)Exel802 (dbf) mutant spermatocytes. Arrows indicate bivalents of the metacentric autosomes. Arrowheads indicate the X-Y pair. n=60 wild-type metaphase spermatocytes; n=54 dbf mutant metaphase spermatocytes, randomly selected from images taken in five experiments. (C) Diagram of the X and Y chromosomes. Red boxes indicate rRNA loci. The fluorescently labeled probe used in fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis is complementary to the 240 bp repeat in the spacers of the rDNA repeats. XL and XR indicate the left and right arms of the X chromosome; YS and YL indicate the short and long arms of the Y chromosome. (D) Fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis in wild-type and dbf z3318/Df(2L)Exel802 (dbf) mutant spermatocytes at metaphase (stage M2/M3) using a fluorescently labeled 240 bp probe (red). DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). n=53 wild-type metaphase spermatocytes; n=20 dbf mutant spermatocytes randomly selected from images taken in five experiments. Scale bars: 10 µm.