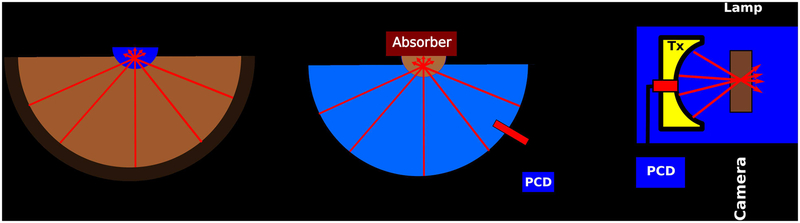
Figure 2:
(A) Schematic of Experiments 1 and 2. The bowl of a clinical, hemispherical transducer array was filled with various aqueous, suspended magnetite nanoparticle coupling baths and imaged by MRI. The transducer also insonated a gel target while MRI thermometry monitored thermal deposition. (B) Schematic of Experiment 3. The transducer in (A) was filled with degassed water and used to insonate various aqueous, suspended magnetite nanoparticle mixtures suspended in a small holder and backed by an acoustic absorber. PCD detectors were used to record cavitation activity. (C) Schematic of Experiment 4. A shock-scattering histotripsy transducer (Tx) was placed in a water tank and directly insonated various coupling baths located in an acoustically transparent holder. A high speed camera and passive cavitation detector (PCD) were used to record cavitation activity.