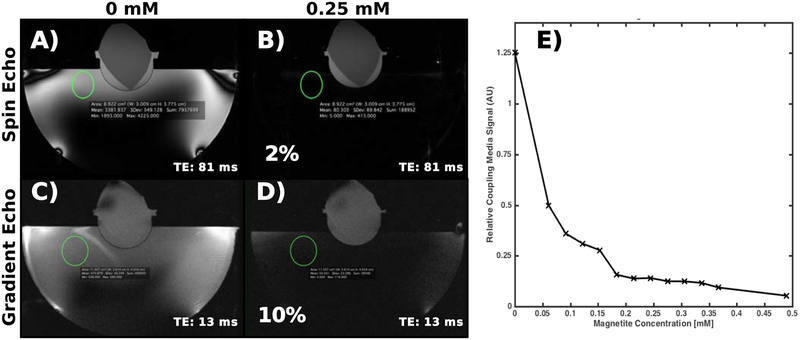
Figure 3:
(A-D) Example spin-echo and gradient-echo images of the gel target using two different nanoparticle concentrations in the coupling bath. The 0.25 mM nanoparticle concentration suppresses the water bath signal by 98% and 90% in the spin-echo and gradient-echo images, respectively. (E) Signal magnitude in the coupling bath in the turbo spin echo images relative to that of the gel as a function of nanoparticle concentration. The coupling bath signal magnitude decreases with an apparently multi-exponential curve, with the majority of signal loss occurring in the first concentration step.