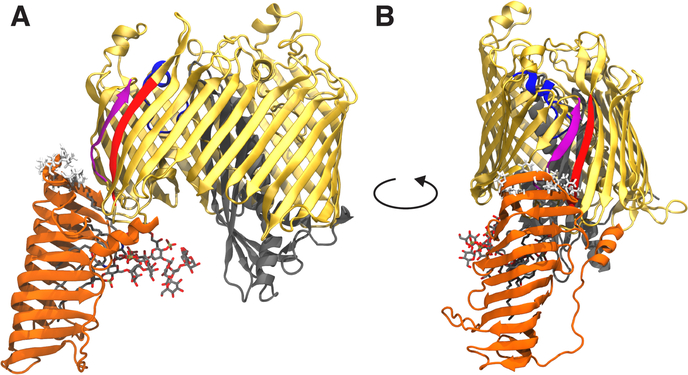
Figure 1:
Front (A) and side (B) views of LptDE with an LPS molecule bound in the N-terminal β-jellyroll domain. The structure is taken from the Sf-LPS simulation at approximately 1900 ns into the simulation. The LptD β-barrel domain is shown in gold with the β1 strand in purple, β26 strand in red, extracellular loop L4 in blue and N-terminal domain in orange. LptE is shown in gray. The LPS molecule is shown in sticks with C, O, N, and P atoms in gray, red, blue, and tan, respectively. Hydrophobic residues predicted to embed into the outer membrane (based on Orientations of Proteins in Membranes database [23]) are shown in white sticks. The main dynamical features of LptDE observed in the equilibrium simulations were a large change in the angle of the N-terminal domain, a separation of the LptD β-barrel seam strands induced by the presence of the substrate, and a significant movement of L4 toward the periplasm.