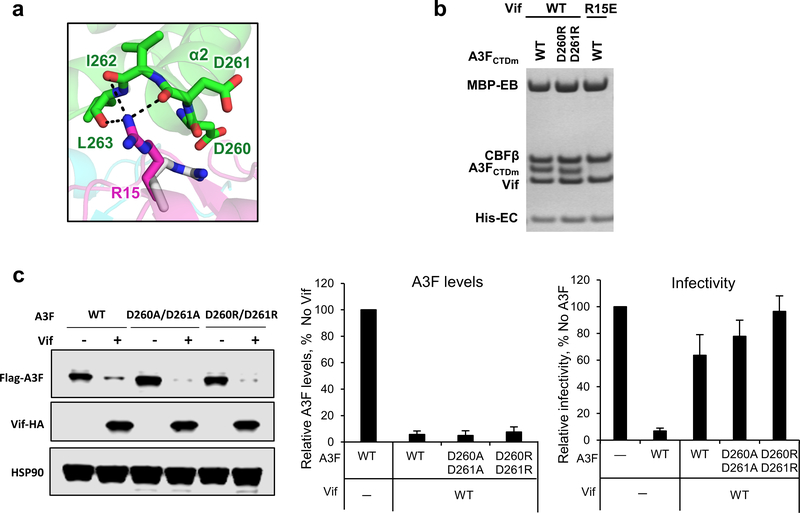
Extended Data Fig. 5. Vif R15 is located at the C-terminus of A3FCTDm α2 helix interacting with the backbone carbonyls of the helix.
a, Upon A3F binding, Vif R15 flips away from the position (gray) pointing into the molecule core to electrostatically interact with the backbone carbonyls of A3FCTDm α2 helix rather than the side chain carboxylates of D260/D261. b, Mutational analysis of the interactions by in vitro binding assay using MBP-tagged Vif–CBFβ–EloB–EloC variants to pulldown A3FCTDm variants. The D260R/D261R double mutation did not affect the Vif interaction. The loading controls are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1b & c. c, The effect of D260A/D261A or D260R/D261R double mutants on A3F sensitivity to Vif-mediated degradation indicated by western blot (left), quantified A3F levels relative to No Vif (mean ± s.d.; n=3 biologically independent experiments; middle), and relative infectivity (mean ± s.d.; n=3 biologically independent experiments; right). Both alanine and arginine mutants did not confer resistance, indicating that the side chains of the residues are not involved in the Vif interaction.