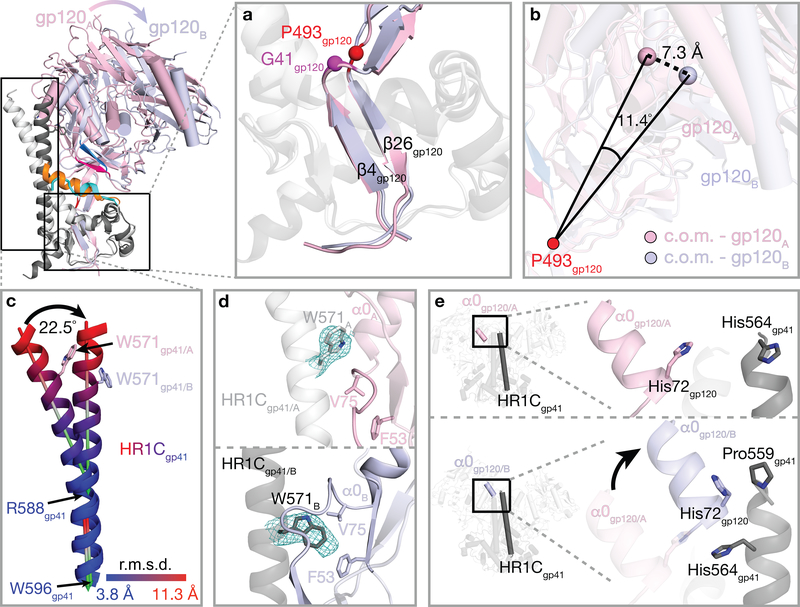
Figure 4. Protomers A and B exhibit different structural features (see also Supplementary Video).
Top left, overlay of cartoon representations of gp120 conformations A (pink) and B (light blue) and gp41 conformations A (light grey) and B (dark grey). Insets show close-up views of features discussed in the text. a, Superimposition of gp120 β4 and β26 strands in protomers A and B. b, Definition of lines joining the hinge residue Pro493gp120 to the center of mass (c.o.m.) of the gp120s in conformations A and B. The lines differed by an angle of 11.4° and a displacement of 7.3 Å. c, Differences in the protomer A and B HR1C helices. After superimposition of gp120 β4 and β26 strands in protomers A and B (panel a), the C-terminal portion of the HR1C helix (Arg588gp41–Trp596gp41) was similar between the two conformations (angle between the two helical axes of 2.5°), whereas the N-terminal portion (Leu565gp41–Glu584gp41) showed deviations up to 11.3 Å at the helix N-termini and a helical axis angle difference of 22.5°. d, Comparison of the location and conformation of gp41 HR1C residue Trp571gp41 in protomer conformations A (top) and B (bottom). e, The gp120 α0 helix in conformation B, but not conformation A, facilitates an extension of the gp41 HR1C N-terminus of a neighboring protomer.