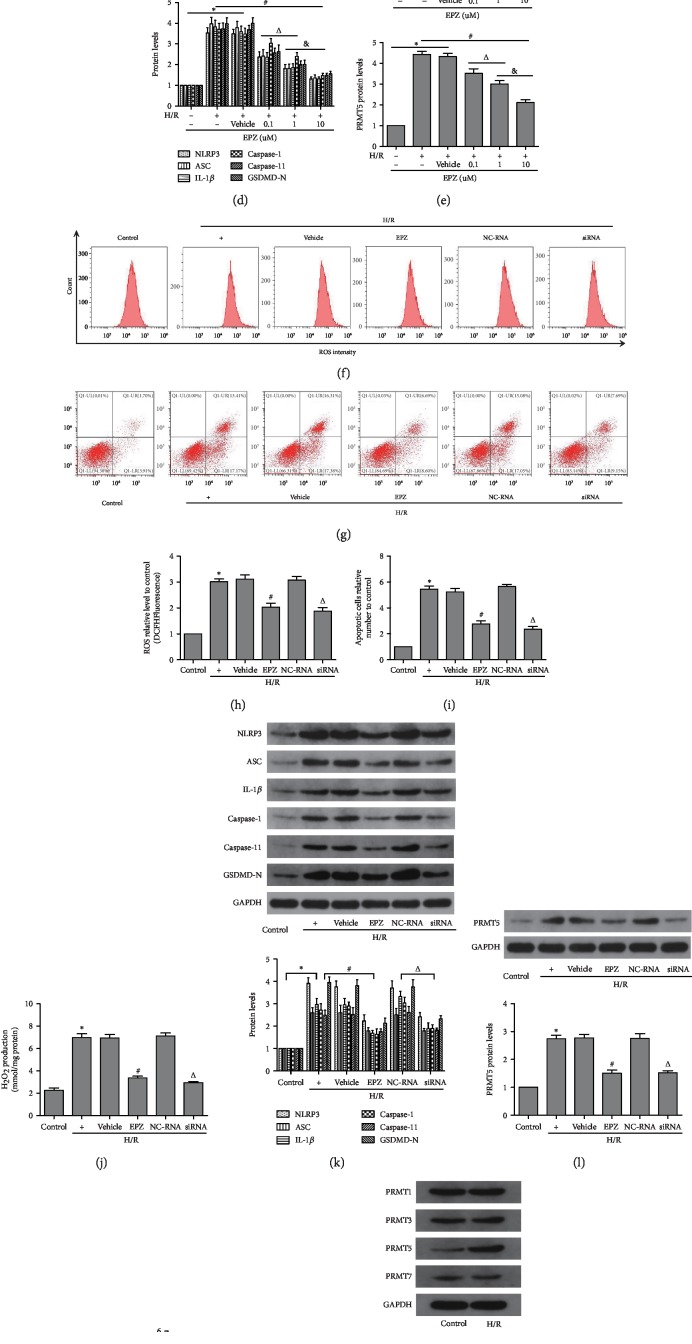
Figure 5.
PRMT5 inhibition attenuated H/R-induced pyroptosis in HK-2 cells. (a, b) The cell viability in different EPZ concentration groups of normal HK-2 cells and H/R HK-2 cells was measured by CCK-8, respectively. (c–e) Pyroptosis-related protein levels and PRMT5 protein levels were detected by western blot analysis after application of EPZ with different concentration. (f, h) The levels of oxidative stress in different intervention groups of HK-2 cells was measured by flow cytometry. (g, i) The apoptosis in different intervention groups of HK-2 cells were measured by flow cytometry. (j) An Amplex Red assay was used to show levels of hydrogen peroxide in different intervention groups of HK-2 cells. (k, l) Pyroptosis-related protein levels and PRMT5 protein levels were detected by western blot analysis in different intervention groups of HK-2 cells. (m) Pyroptosis-related protein mRNA levels were detected by real-time RT-PCR in different intervention groups of HK-2 cells. (n) Different subtypes of PRMT were measured by western blot analysis in the H/R group of HK-2 cells. Values were expressed as the mean ± SEM. (a, b, d, and e) ∗P < 0.05, relative to the control group; #P < 0.05, relative to the H/R group; ΔP < 0.05, relative to the group with 0.1 uM EPZ. &P < 0.05, relative to the group with 1 uM EPZ, n = 6. (h–n) ∗P < 0.05, relative to the control group; #P < 0.05, relative to the H/R group; ΔP < 0.05, relative to the NC-RNA group, n = 6. H/R: hypoxia/reoxygenation; ROS: reactive oxygen species; EPZ: EPZ015666; PRMT5 inhibitor; siRNA: small interfering RNA specific to PRMT5; NC-RNA: nontargeting siRNAs.