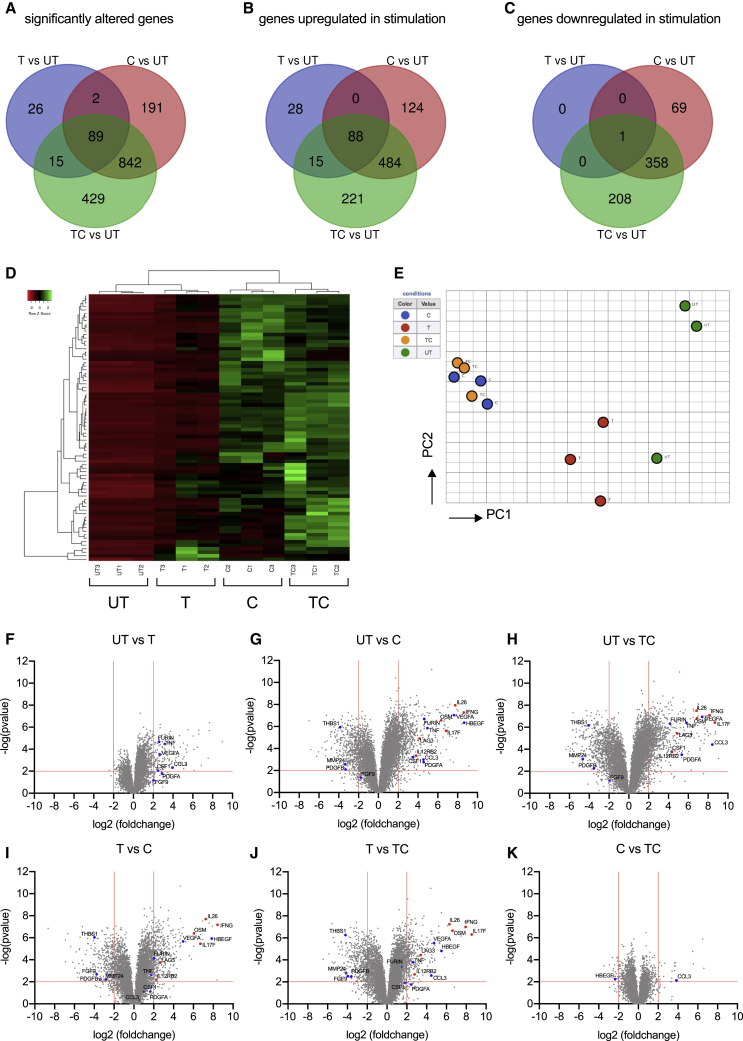
Figure 4.
TCR- and Cytokine-Activated MAIT Cells Possess Distinct Transcriptional Profiles
(A–C) Venn diagrams showing genes that are significantly differentially modulated (p < 0.05, fold change > 4) in TCR (T)-, cytokine (C)-, or TCR and cytokine (TC)-treated CD8+ MAIT cells compared with untreated (UT) MAIT cells of three healthy individuals. The cytokine (C) stimulation consisted of a cocktail of 4 cytokines: IL-12 (2 ng/mL), IL-18 (50 ng/mL), IL-15 (25 ng/mL), and TL1A (100 ng/mL). Genes with significantly altered expression levels (A) are divided into two sets: those are that are upregulated upon stimulation (B) and those that are downregulated upon stimulation (C).
(D) Heatmap showing 1,594 significantly differentially expressed transcripts (p < 0.05, fold change > 4) between TCR/C/TC-stimulated and UT CD8+ MAIT cells among the same three healthy individuals.
(E) Visualization of the CD8+ MAIT cell transcripts elicited by differential stimulations in the subspace of the first principle components (PCs). Each colored circle represents a sample and is color coded in accordance with the conditions with which cells were stimulated, as illustrated on the right-hand side of the graph.
(F–K) Volcano plots to visualize differentially expressed transcriptional profiles of activated CD8+ MAIT cells stimulated in different ways. Each point represents a single gene, and genes expressed at significantly higher or lower levels between the compared conditions are depicted, respectively, in the upper-right or upper-left corner of each plot. Genes discussed in the text are highlighted in blue (tissue repair associated) or in red (inflammation associated). The gene expression of untreated MAIT cells was compared to (F) T-, (G) C-, or (H) TC-stimulated MAIT cells. Further, gene expression in those cells was also compared directly between the different stimulation conditions: (I) T- to C- stimulation, (J) T- to TC-stimulation, and finally (K) C- to TC-stimulation.
Data were acquired from three donors in one experiment.