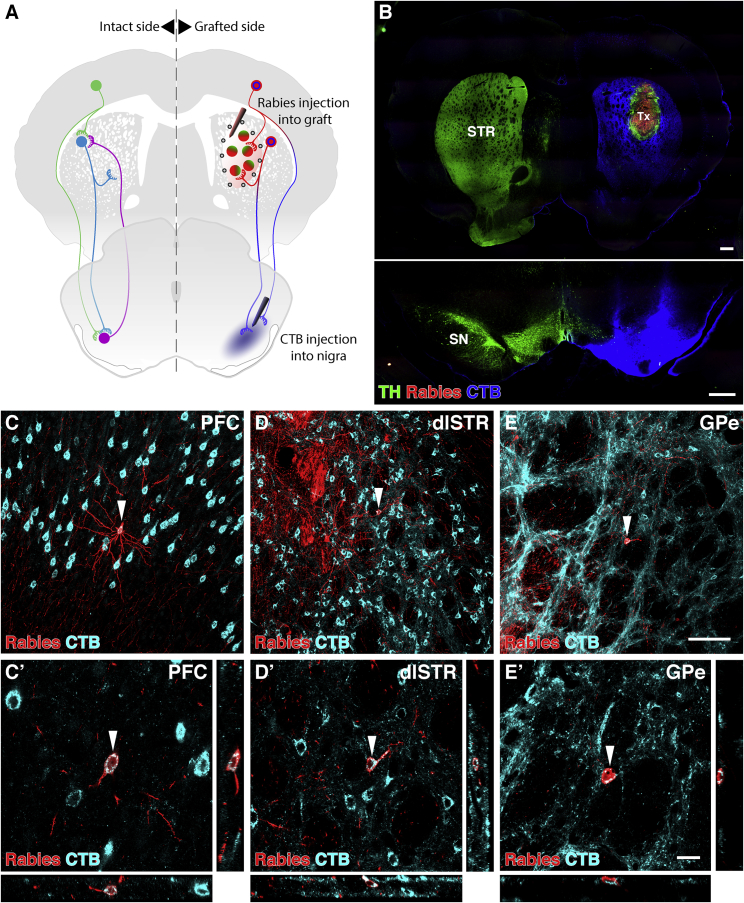
Figure 6.
Host Neurons Providing Monosynaptic Input to VM-Patterned Grafts Placed in the Striatum Simultaneously Collateralize on Neurons in the Substantia Nigra
(A) Schematic of monosynaptic EnvA ΔG-rabies tracing initiated from striatal grafts, with simultaneous conventional retrograde cholera toxin subunit B (CTB) tracing of projections to the substantia nigra.
(B) Sections through striatum depicting the graft and rabies injection site, and the substantia nigra depicting the lesion and CTB injection site.
(C–E) Host prefrontal cortical (C), medium spiny striatal (D), and pallidal neurons (E) were labeled with both CTB and rabies. Arrowheads indicate neurons imaged with confocal microscopy in (C’), (D’), and (E’). These neurons simultaneously synapse with graft neurons and maintain a collateral projection to the substantia nigra.
Scale bars represent 500 μm (B), 100 μm (C, D, and E), and 20 μm (C’, D’, and E’). Images in (B) is digitally stitched from multiple high-magnification images. CTB, cholera toxin subunit B; dlSTR, dorsolateral striatum; GPe, external globus pallidus; PFC, prefrontal cortex; SN, substantia nigra; STR, striatum; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; Tx, transplant.