Figure 3.
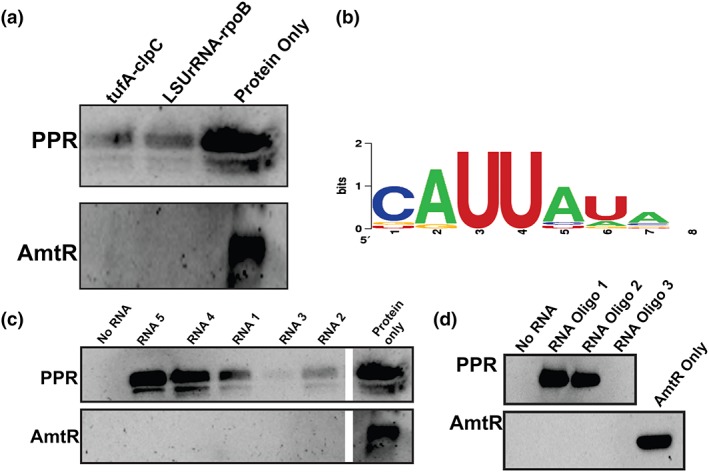
PfPPR1 binds RNA. (a) Pull‐down assay showing that in vitro transcribed apicoplast RNA transcripts (tufA‐clpC and LSUrRNA‐rpoB) binds to PfPPR1, as shown by Western blot analysis. (b) Weblogo of sequences enriched by SELEX, the height of the letter corresponds to the frequency of that nucleotide at that position. (c) RNA transcribed from five clones identified from the final SELEX round were used in a pull‐down experiment. Each 150‐nt RNA molecule contained a constant 125‐nt region (not shown) and a variable 25‐nt region (shown below). Consensus sequences and sequences with slight variation from the consensus are underlined. As a control, RNA pull‐downs were also performed with AmtR. Loading controls are shown to the right of the gel. (d) PfPPR1 pull‐downs with biotinylated RNA oligonucleotides (sequence shown below) each containing the consensus sequence followed by either a U (RNA oligo 1, underlined) or an A (RNA oligo 2, underlined) and a randomly generated six nucleotide sequence (underlined in RNA oligo 3) using an anti‐His antibody demonstrated specificity of PPR for the consensus sequence. The control protein AmtR did not interact with any of the RNA oligonucleotides tested. A repeat of this experiment showed the same results (Figure S8) RNA1 UUAAACUUGAUGCCCGGCGUUUCAG RNA2 UUACCGCGCGUAACACCGGGCCUGU RNA3 UUCGGCGACGGAAAGAGUGAAUCCG RNA4 UUGUAUUUAUUUAAAAAAUUAUGU RNA5 UUAUAACUCGCCUAGACGGGAUUAU RNA oligo 1 ACGACAUUAUAUGGUCGGA RNA oligo 2 ACGACAUUAUAAGGUCGGA RNA oligo 3 ACGACAUGACGAGGUCGGA
