Figure 3.
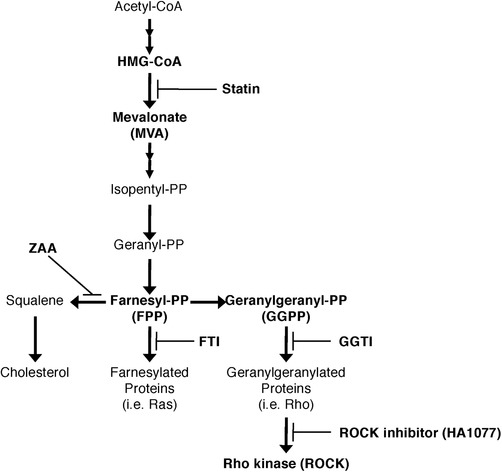
Schematic of the mevalonate pathway, showing the sites of action of statins and other inhibitors. Statins inhibit the conversion of 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐CoA (HMG‐CoA) to mevalonate and thus inhibit the downstream synthesis of not only cholesterol, but also isoprenoid intermediates, such as farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), which regulate posttranslational modifications of the small GTPase Ras and Rho families. Zaragozic acid A (ZAA), farnesyl transferase inhibitor FTI‐277, and geranylgeranyl transferase inhibitor GGTI‐298 block the synthesis pathways that split off from FPP in the mevalonate pathway. HA1077 blocks the pathway of Rho kinase (ROCK).
