Figure 2.
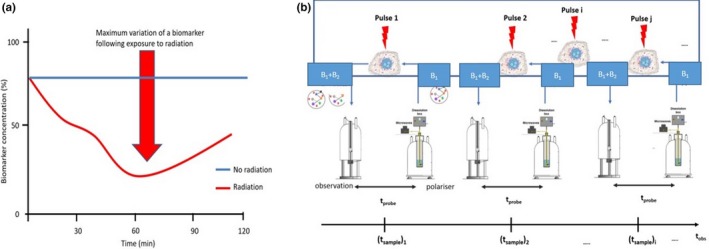
a) Biomarker detection strategy using molecular imaging based on hyperpolarized (DNP‐enhanced) magnetic resonance for following radiotherapy effects. Free radicals and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species produced by radiation‐triggered mechanisms on a timescale of several hours alter the concentration of detected biomarkers. The figure is adapted from Ref. [58] b) Experimental setup for the observation of radiation effects in cell serving as a test laboratory for imaging‐oriented radiotherapy in vivo. B1 and B2 are biomolecular markers sensitive to radiation effects exerted via reactive molecular species (free radicals), t probe < 5 min for most endogenous molecules, and t obs is on the order of tens of minutes to hours. For in vivo detection, an MRI scanner replaces the observation spectrometer. DNP, Dynamic Nuclear Polarization.
