Figure 1.
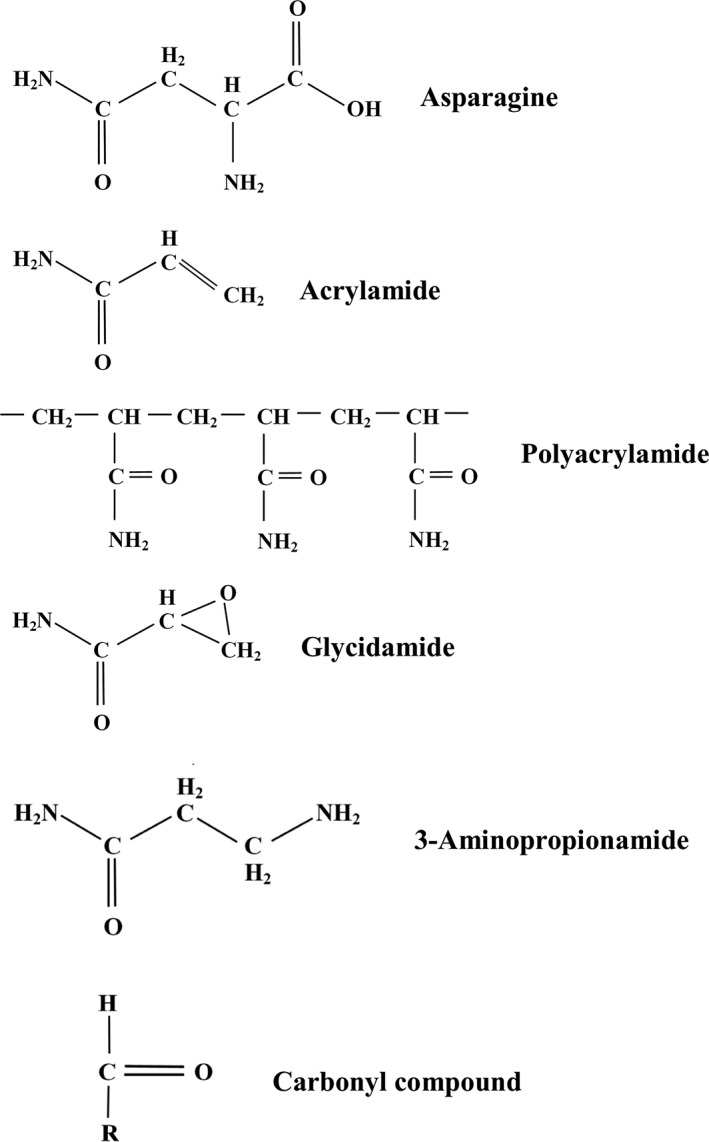
Diagram showing the structures of, from top to bottom, asparagine (C4H8N2O3), acrylamide (C3H5NO), acrylamide chains in polyacrylamide, glycidamide (C3H5NO2) (a metabolite of acrylamide), 3‐aminopropionamide (C3H8N2O) (an intermediate in one of the pathways proposed for acrylamide formation), and a carbonyl compound
