Figure 5.
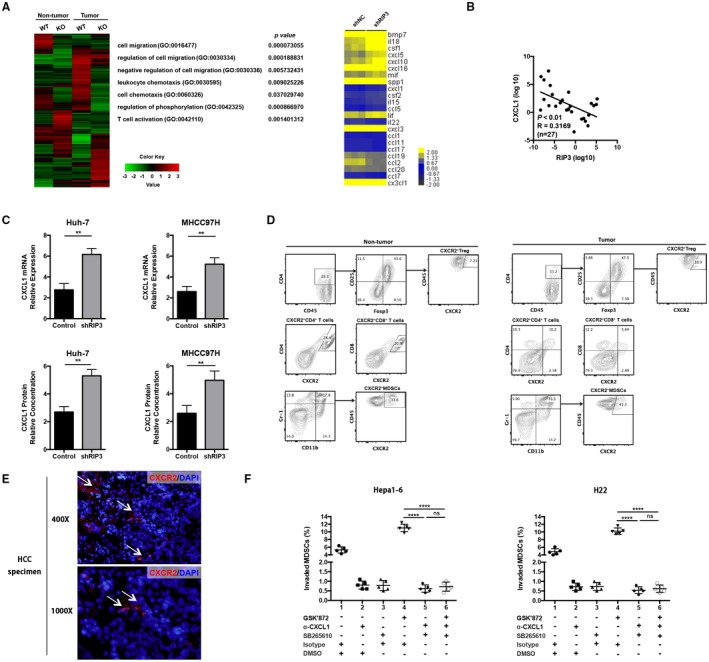
RIP3 deficiency up‐regulates CXCL1 and induces MDSC chemotaxis through the cognate receptor CXCR2. (A) Gene microarray imaging (left panel) and RT2 profiler PCR array (right panel) were performed for screening dysregulated hepatoma‐derived genes and pathways. The top 10 variable genes were listed. (B) Correlation analysis between RIP3 and CXCL1 by quantitative real‐time PCR using an independent cohort of 27 patients. (C) RT‐PCR and ELISA of human HCC cell lines Huh‐7‐shNC and Huh‐7‐shRIP3 (left panel) and MHCC97H‐shNC and MHCC97H‐shRIP3 (right panel). **P < 0.01. (D) Representative flow‐cytometric images of CXCR2+ cells in Tregs, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and MDSCs. (E) Representative immunofluorescence of CXCR2+ cells in human HCC tissues. Upper, ×400; lower, ×1,000. (F) Chemotaxis response of murine MDSCs treated with GSK’872, α‐CXCL1, and SB265610 in the presence of Hepa1‐6 or H22 CM, respectively. Left, Hepa1‐6; right, H22. Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GO, gene ontology; ns, nonsignificant.
