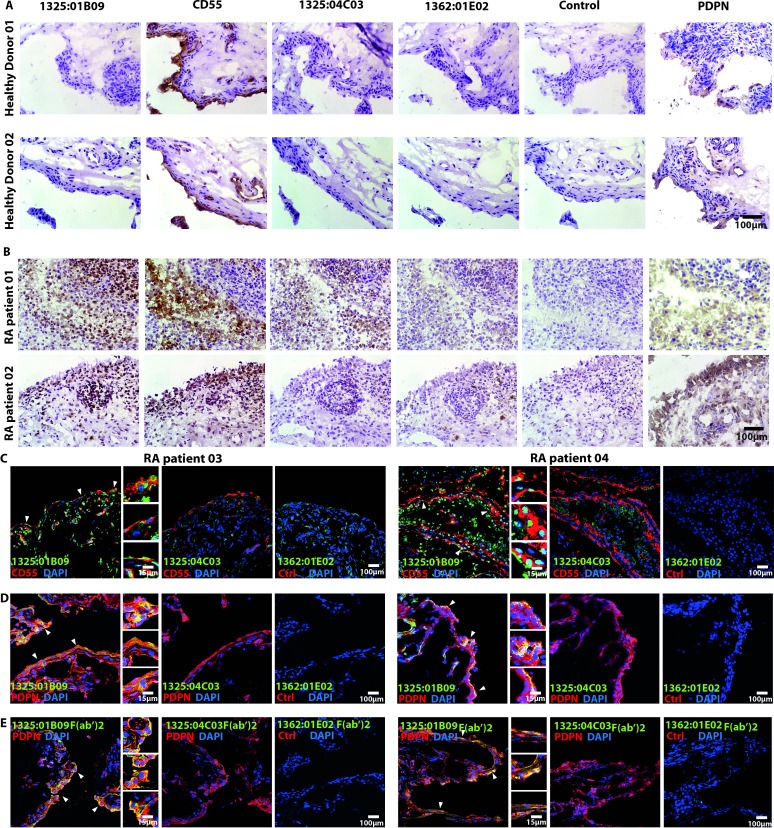
Figure 6.
The monoclonal ACPA clones 1325:01B09 and 1325:04C03 bind to synovial targets in patients with RA but not in healthy controls. The immunohistochemistry images illustrate binding patterns of the monoclonal ACPA clones 1325:01B09 and 1325:04C03 to synovial tissues obtained from healthy donors (A) or patients with RA (B). Mouse IgG1 and the non-citrulline-specific 1362:01E02 (E02) monoclonal antibody were used as controls. CD55 and podoplanin (PDPN) stainings highlight FLS-rich areas of the synovial membrane. Immunohistochemistry stainings were analysed with light microscopy using 250x original magnification. (C) Confocal microscopy images illustrate a partial colocalisation of the ACPA clone 1325:01B09 with CD55 (C) and PDPN (D), highlighted by closed arrows. Stainings with the monoclonal ACPA 1325:04C03 and the control 1362:01E02 antibodies are also shown. Moreover, partially colocalisation of 1325:01B09 F(ab’)2 with PDPN were highlighted by arrows (E). An original magnification of 400x was used for confocal microscopy. ACPA, anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody; DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FLS, fibroblast-like synoviocytes; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.