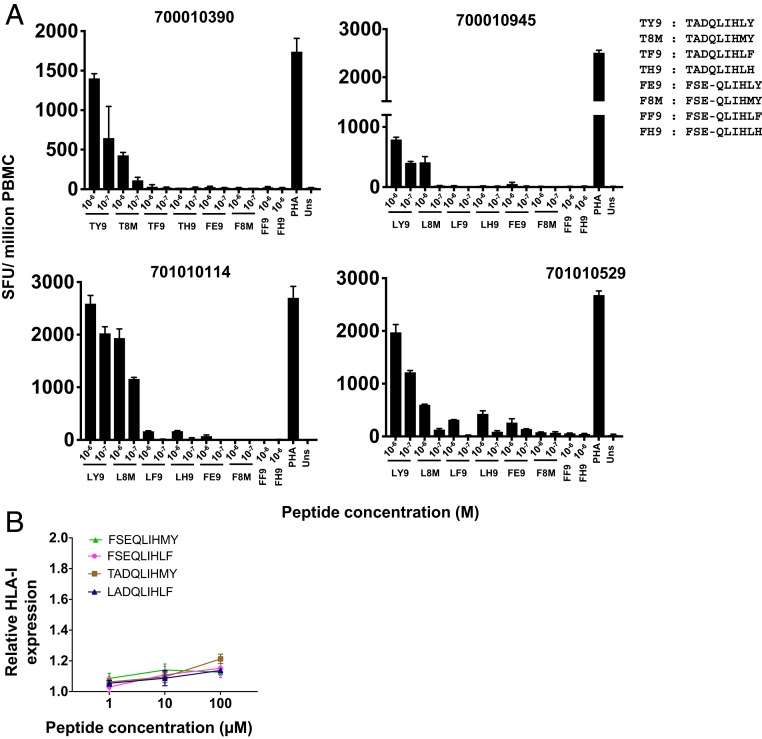
Fig. 6.
Mutations abrogate CD8+ T cell recognition of both contiguous and spliced epitopes. (A) Responses detected to mutant contiguous LADQLIHMY (L8M), LADQLIHLF (LF9), and LADQLIHLH (LH9) and mutant spliced FSE-QLIHMY (F8M), FSE-QLIHLH (FH9), and FSE-QLIHLF (FF9) peptides in cultured IFN-γ ELISpot assays following T cell expansion by in vitro culture with autologous contiguous viral epitopes LADQLIHLY (LY9) or TADQLIHLY (TY9). Data are expressed as SFU per million PBMC, and the mean ± SD of duplicate wells are shown. (B) RMA-S HLA-I stabilization assays comparing the relative binding affinities of dominant mutant versions of the nonspliced (LADQLIHLF and TADQLIHMY) and spliced (FSE-QLIHLF and FSE-QLIHMY) viral epitopes to HLA-A*01:01. Data are expressed as the mean relative fluorescence values ± SD from triplicate experiments.