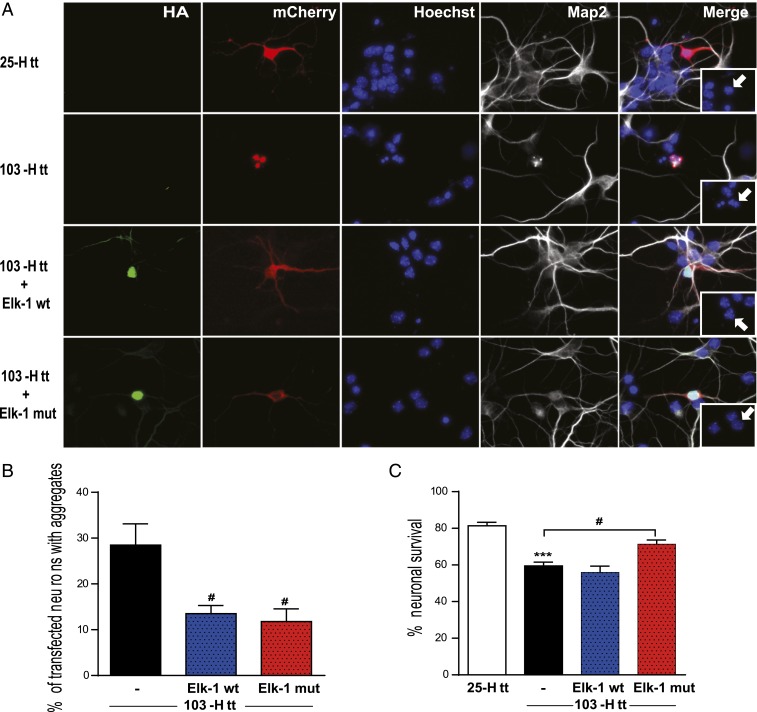
Fig. 4.
Elk-1 exerts beneficial effects in a primary striatal neuron culture model of HD. (A) Representative images of primary mouse striatal neurons transfected on DIV6 (in vitro day 6 in culture) with cDNAs encoding 25Q-Htt or 103Q-Htt (mCherry red) with or without HA-tagged versions of Elk-1-wt or Elk-1-mut (3R-Asp-Elk-1) (green). Immunocytochemical detection of MAP2 (grey) and Hoechst (blue) were performed to analyze the neuronal integrity. Note that 103-Htt-expressing neuron shows progressive nuclear localization of aggregates (red), neuritic retraction (grey) and DNA damage (blue). White arrows depict nuclear morphology of transfected neurons. (Magnification in the images and the Insets: 40×.) (B and C) Quantification of aggregate formation (B) and neuronal survival based on Hoechst labeling (C) in neurons were performed in transfected cells 24 h after transfection, from 3 independent experiments (100 transfected neurons per experiment) and expressed as mean ± SEM. ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test. ***P < 0.001, 25Q-Htt-expressing neurons vs. 103Q-Htt-expressing neurons; #P < 0.05, 103Q-Htt-expressing neurons vs. 103Q-Htt/Elk-1-Wt or 103Q-Htt/Elk-1-mut-expressing neurons.