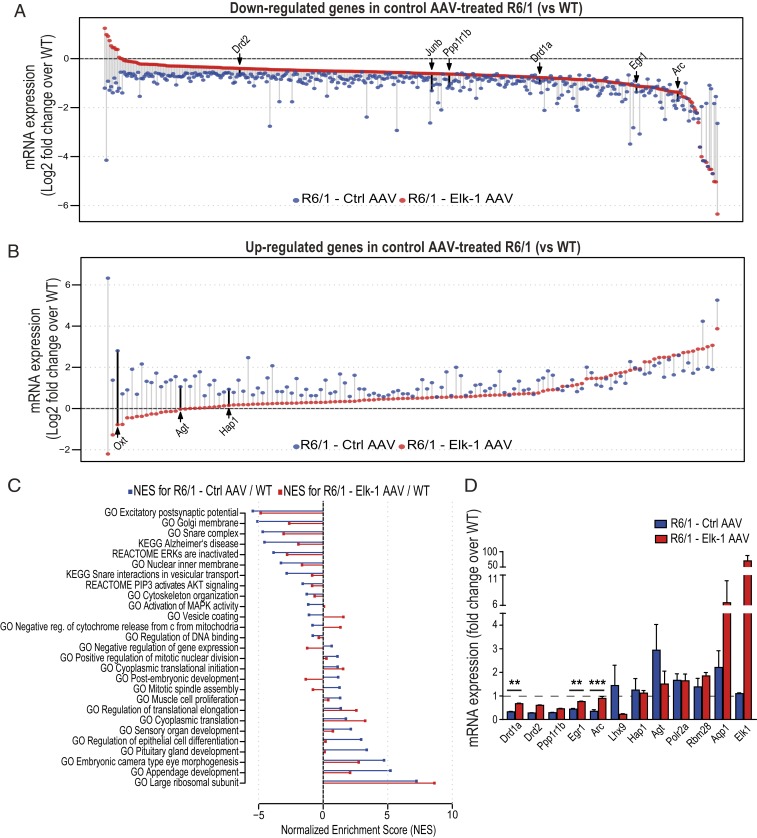
Fig. 5.
AAV-mediated Elk-1 overexpression alleviates dysregulation of genes in R6/1 striatum. (A and B) Dot plots showing down-regulated (A) and up-regulated (B) genes determined by RNA-seq in the striatum of R6/1 mice compared to wild-type littermates within the control AAV treatment group. Each data point represents log2 of fold-change value (HD fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads [FPKM]/wild-type FPKM) of a differentially expressed gene in R6/1 treated with Ctrl AAV (blue data points) and in R6/1 treated with Elk-1 AAV (red data points). Several previously identified HD-associated genes are labeled. n = 2 to 4 mice per genotype per group. (C) ssGSEA was performed for Elk-1 AAV- and Ctrl AAV-treated R6/1 striatal transcriptomes using log2 of fold-changes (compared to Ctrl AAV-treated wild-types) in expression of each gene in order to identify enriched gene sets from the MSigDB. A selection from the most enriched gene sets (FDR < 0.005) in Ctrl AAV-treated R6/1 mice (blue bars) and their enrichment in Elk-1 AAV-treated R6/1s (red bars) are plotted as bar graphs. Gene sets enriched in up-regulated genes in HD have positive enrichment scores, while those that are down-regulated in HD have negative enrichment scores. Standard names of the gene sets from the MSigDB are listed on the plot. NES, normalized enrichment score. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR confirmation of the expression of several key dysregulated genes (Drd1a, Drd2, Egr-1, Arc, Ppp1r1b, Lhx9, Hap1, Agt, Polr2a, Rbm28, Aqp1) in HD as well as of Elk-1 overexpression by Elk-1-expressing AAV (n = 3 to 5 mice per genotype per group). Data presented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. See also SI Appendix, Fig. S4.