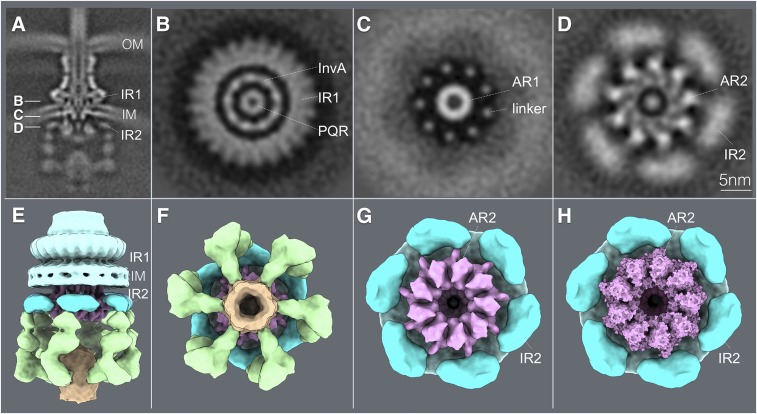
Fig. 6.
Close association of a cytoplasmic ring of InvA with the sorting platform and cytoplasmic domain of the needle complex component PrgH. (A) A vertical section from the in situ cryo-ET structure of the injectisome from WT S. Typhimurium indicating the section planes of the structures shown in B–D. (B–D) Horizontal sections through the planes indicated in B depicting the InvA nonameric ring within the inner ring 1 (IR1) of the needle complex structure (B), the linker region that joins the membrane and cytoplasmic domains of InvA (C), and its tight association with the cytoplasmic domain of the inner ring 2 (IR2) of the needle complex (D). The position of the core component of the export apparatus (labeled PQR) is also shown. (E and F) Side (E) and bottom (F) views of the surface rendering of the cytoplasmic elements of the T3SS injectisome. (G) Bottom view of the T3SS injectisome after removal of the sorting platform elements to highlight the close association between the larger cytoplasmic ring of InvA (AR2) with the cytoplasmic ring of PrgH (IR2). (H) Bottom view of the InvA nonameric ring (AR2) with the overlaid atomic structure of the cytoplasmic domain of an InvA holog (PDB-4A5P). No symmetry was applied in A–D but to visualize the InvA ring, symmetry was applied in E–H. AR1, InvA-associated ring 1; AR2, InvA-associated ring 2. IM, bacterial inner membrane; OM, bacterial outer membrane.