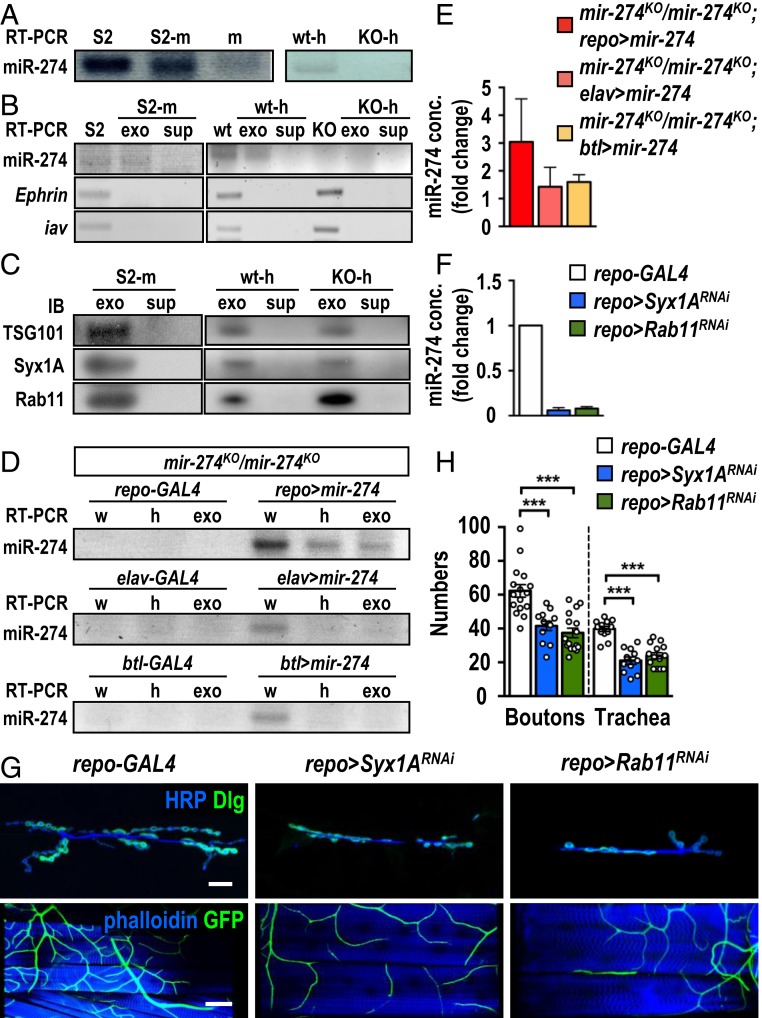
Fig. 3.
Secretion of exosomal miR-274 from glia. (A) Detection of miR-274 by RT-PCR in S2 cells (S2) and S2 cell-cultured medium (S2-m), and non-S2 cell-cultured medium (m) (Left). miR-274 was detected in w1118 hemolymph (wt-h) but not in mir-274KO hemolymph (KO-h) (Right). (B) Detection of mir-274, Ephrin, and iav by RT-PCR in S2 cell lysates (S2), exosomal fractions (exo), and depleted supernatants (sup) from S2-medium (S2-m), w1118 larvae (wt) and mir-274KO (KO) larvae. (C) Detection of TSG101, Syx1A, and Rab11 in Western blots for exosomal fractions (exo) and depleted supernatants (sup) from cultured S2 medium (S2-m), wild-type hemolymph (wt-h), and mir-274KO hemolymph (KO-h). (D) Detection of miR-274 by RT-PCR in the mir-274KO mutant with or without expression of UAS-mir-274 by repo-GAL4 (Top), elav-GAL4 (Middle), or btl-GAL4 (Bottom) in whole larval lysates (w), hemolymphs (h), and exosomal fractions (exo). (E) Quantification of miR-274 levels by absolute qPCR in larval exosomal fractions. (F) Absolute qPCR was performed to detect exosomal miR-274 levels in hemolymphs. (G) Confocal images of synaptic boutons (scale bar: 30 µm) and tracheal branches (scale bar: 60 µm) in repo-GAL4 control, repo > Syx1ARNAi, and repo > Rab11RNAi. (H) Dotted bar graph for quantification of synaptic boutons and tracheal branches. See SI Appendix, Table S2. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc. ***P < 0.001.