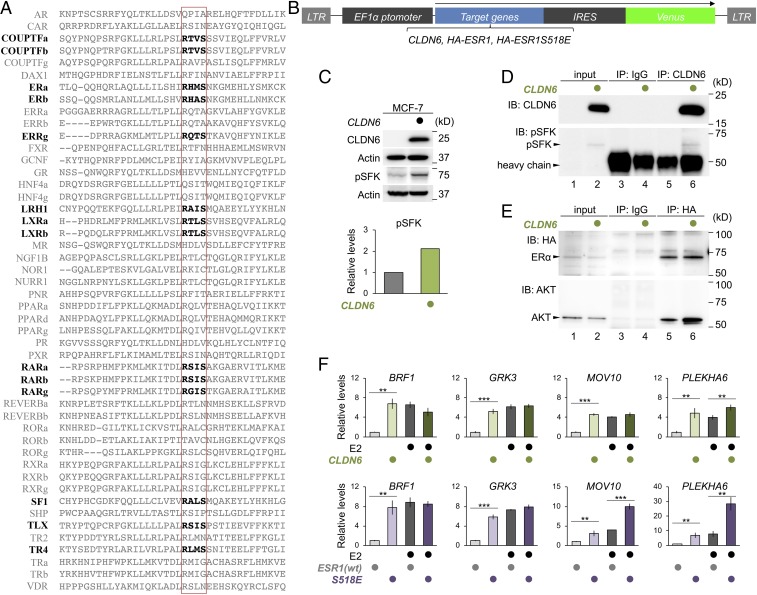
Fig. 5.
The CLDN6-adhesion signaling regulates the ERα activity. (A) Conservation of the AKT phosphorylation motif in human nuclear receptor proteins. The AKT-consensus phosphorylation motif and the corresponding sites in nuclear receptors are indicated in bold and the red rectangle lines, respectively. (B) The construct of CLDN6, HA-ESR1, and HA-ESR1S518E expression vectors. (C) Western blot for the indicated proteins in MCF-7 and MCF-7:CLDN6 cells. Quantification of the protein levels is shown in the histogram. (D) Association between CLDN6 and pSFK in MCF-7:CLDN6 cells. In the input lanes, 2% of the input protein samples were loaded. (E) Association between AKT and HA-ERα in MCF-7:HA-ESR1 and MCF-7:CLDN6:ESR1 cells. In the input lanes, 1% for HA or 0.1% for AKT of the input protein samples were loaded. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR for the indicated molecules in the MCF-7 cells. The cells were treated for 24 h with vehicle (ethanol) or 1.0 µM Estradiol (E2). The relative expression levels are shown in the histograms (mean ± SD; n = 4). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.