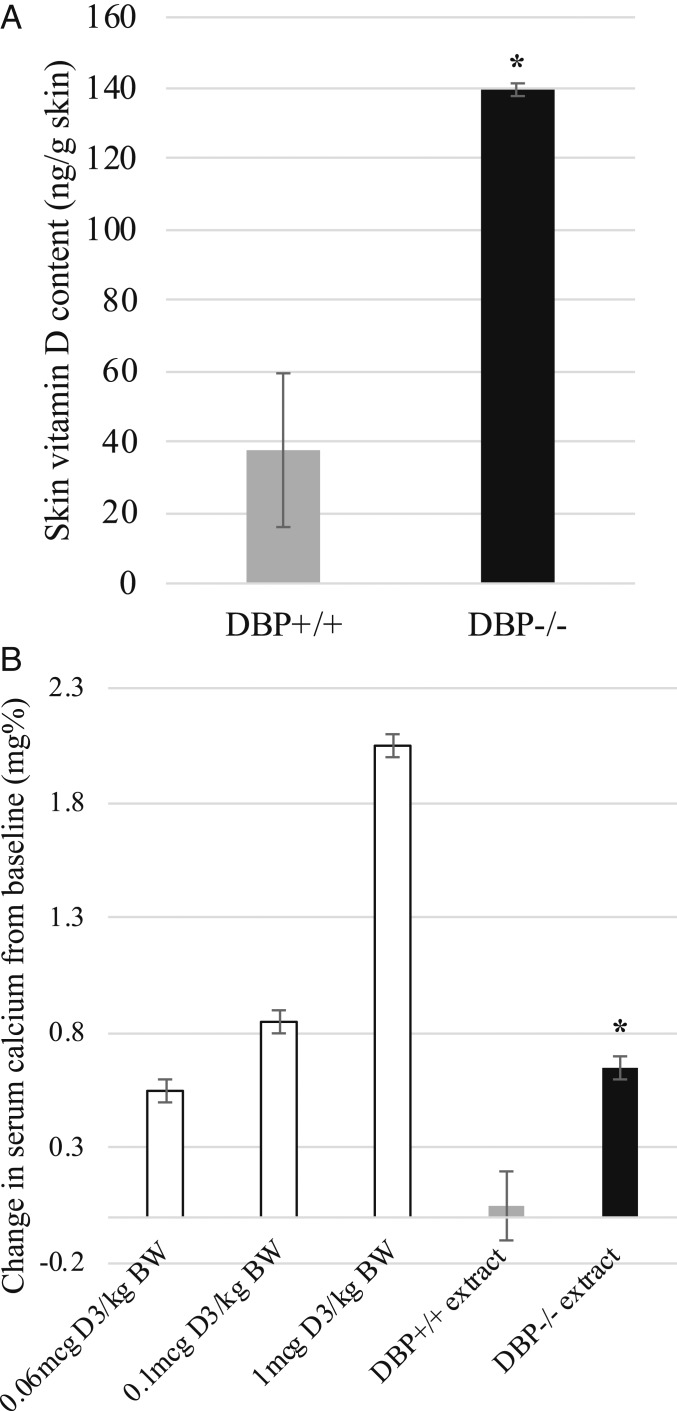
Fig. 4.
Vitamin D content in skin was lower in DBP+/+ mice than in DBP−/− mice 48 h following 4 daily UVB treatments. (A) HPLC analysis of skin lipid extracts revealed vitamin D content was lower in DBP+/+ mice compared to DBP−/− mice (n = 3, ± SEM, *P < 0.05 vs. DBP+/+). (B) Serum calcium response of vitamin D-deficient rats administered either DBP−/− mouse skin extract or DBP+/+ skin extract. Vitamin D activity remained in the DBP−/− while in contrast, no vitamin D activity was detected in DBP+/+ mouse skin extracts. Three control groups were included that were administered vitamin D in place of skin extracts (n = 2 rats per experimental group, n = 2 mice per extract, ± SEM, *P < 0.05 vs. DBP+/+ extract).