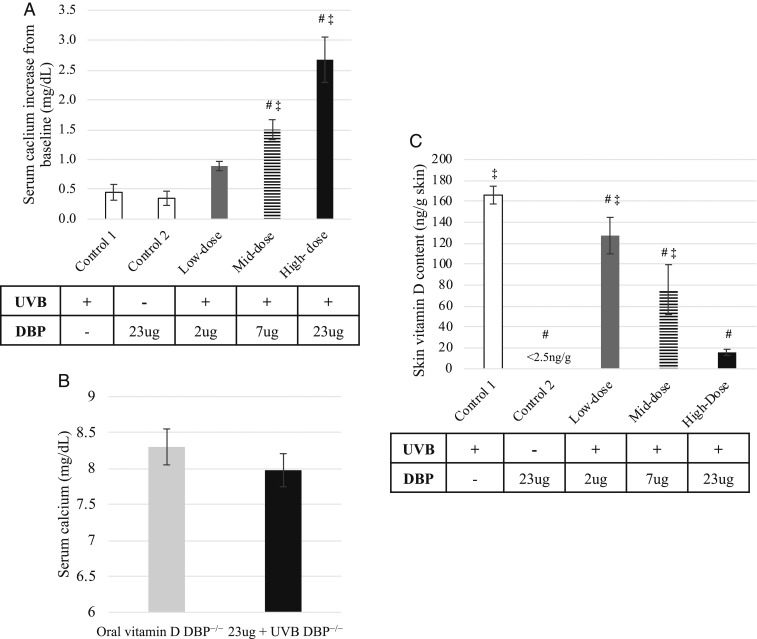
Fig. 5.
Repletion of DBP by i.v. injection of recombinant DBP prior to UVB treatments resulted in increased serum calcium and decreased skin vitamin D levels in DBP−/− mice. Serum calcium measurements were taken 24 h after the last of 2 daily treatments. (A) Injection of increasing amounts of recombinant mouse-DBP prior to UVB treatment resulted in a corresponding increase in serum calcium of DBP−/− mice (n = 4 for control dose groups, n = 5 recombinant protein dose groups, ± SEM, #P < 0.05 vs. control 1, ‡P < 0.05 vs. control 2). (B) Serum calcium was normalized in DBP−/− mice administered 2 daily injections of 23 µg of DBP together with UVB treatment compared to vitamin D (orally) sufficient DBP−/− mice maintained on standard chow diet (n = 5 for 23 µg dose group, n = 3 for control group, ± SEM). (C) HPLC analysis of skin lipid extracts obtained 48 h following UVB irradiation revealed a corresponding decrease in skin vitamin D content with increasing amounts of DBP injected compared to control 1 (n = 3, ± SEM, #P < 0.05 vs. control 1, ‡P < 0.05 vs. control 2).