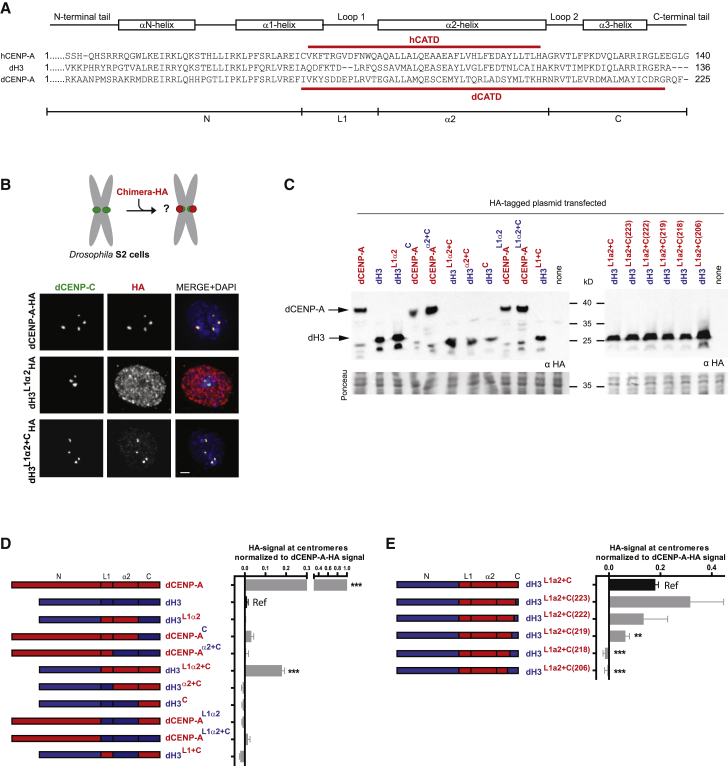
Figure 1.
The CATD of CENP-A in Drosophila Is Larger than in Humans and Includes the α3 Helix
(A) Drosophila CENP-A was divided into four domains: the N-terminal N from residues 1 to 160 (corresponding to residues 1 to 75 in dH3); the L1 domain from residues 161 to 173 contains loop L1 (residues 76 to 86 in dH3); the α2 domain, which contains helix α2 (residues 174 to 202 in dCENP-A and residues 87 to 115 in dH3); and the C-terminal C from residues 203 to 225 (residues 116 to 136 in dH3).
(B) Experimental scheme and representative IF images of HA-tagged WT dCENP-A, dH3L1α2, and dH3L1α2+C chimera expression patterns in S2 Drosophila cells. dCENP-C marks Drosophila centromeres.
(C) Western blot analysis of expression levels of HA-tagged dCENP-A/dH3 chimeras using α-HA antibody.
(D and E) Quantitation of indicated HA-tagged dCENP-A/dH3 chimera mean intensities at centromeres normalized to HA-tagged dCENP-A mean intensity at centromeres.
Scale bar, 1μm. Error bars show SEM. Asterisks denote significant differences (∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001); absence of an asterisk denotes a non-significant difference. The reference sample for statistical analysis is indicated as Ref.