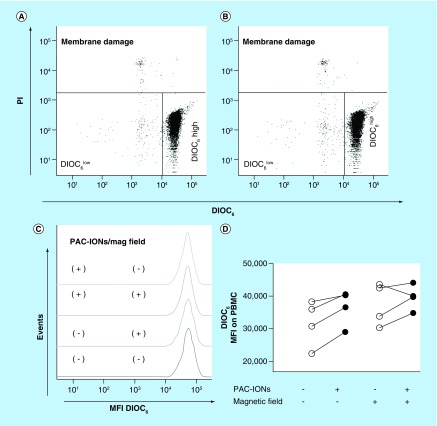
Figure 1. . The poly(acrylic acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles and the magnetic field do not affect either the cell membrane integrity or the mitochondrial membrane potential of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Flow cytometer dot plots showing DIOC6 and PI staining of PBMCs that were cultured in the absence (A) or presence (B) of the PAC-IONs. The percentages of DIOC6 high (viable), DIOC6 low (mitochondrial damage) and PI+ (with membrane damage) cells of a representative experiment are shown. The DIOC6 MFI of the viable PBMCs was compared by histogram overlay: PBMCs cultured with and without PAC-IONs, and exposed or not to the magnetic field (C). The consolidated values of DIOC6 MFI were compared through an analysis of variance, ANOVA II (D); n = 4 independent experiments.
ANOVA: Analysis of variance; MFI: Mean fluorescence intensity; PAC-ION: Poly(acrylic acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticle; PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell; PI: Propidium iodide.