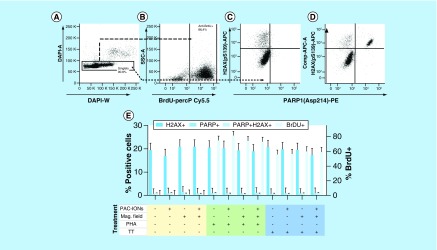
Figure 2. . The poly(acrylic acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles and the magnetic field do not affect the capacity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to proliferate and do not induce DNA damage or caspase-3-mediated cell death.
(A) Flow cytometer dot plots show the strategy for the exclusion of cell aggregates based on DAPI-A versus DAPI-W. (B) Definition of BrdU+ PBMCs. (pS139) H2AX+ and cleaved PARP1+ cells in PBMCs treated or not with the PAC-IONs and exposed to the MF (C). Positive control of cell damage: PBMCs were treated with 20 nM Topotecan hydrochloride (D). Consolidated results (E) Y1 axis, percentage of (pS139) H2AX+ and/or cleaved PARP1+ cells. Y2 axis, percentage of BrdU+ cells. Comparisons were made with ANOVA II, n = 5 independent experiments.
ANOVA: Analysis of variance; MF: Magnetic field; PAC-ION: Poly(acrylic acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticle; PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell.