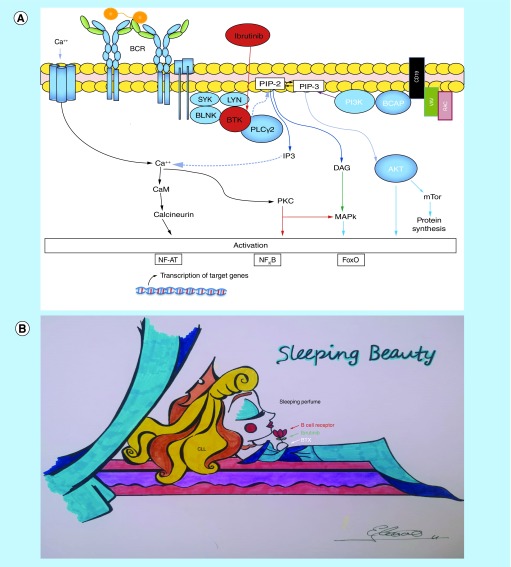
Figure 3. . Sleeping Beauty effect.
(A) Ibrutinib is a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which increases the apoptotic susceptibility of malignant lymphocytes and also causes tissue redistribution of tissue-resident chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells into the blood with rapid shrinkage of the lymph nodes. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is essential for chemokine-mediated homing and adhesion of B cells, and for the activation of several pathways, contributing to chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival, including AKT, and NF-κB pathways. Combinations such as ibrutinib and obinutuzumab or ibrutinib and venetoclax may be safe and effective treatment options. (B) ‘The Sleeping Beauty effect’. The drawing exemplifies a dormant CLL cell breathing the scent of the sleep spell when ibrutinib inhibits Bruton's tyrosine kinase.
CLL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia.