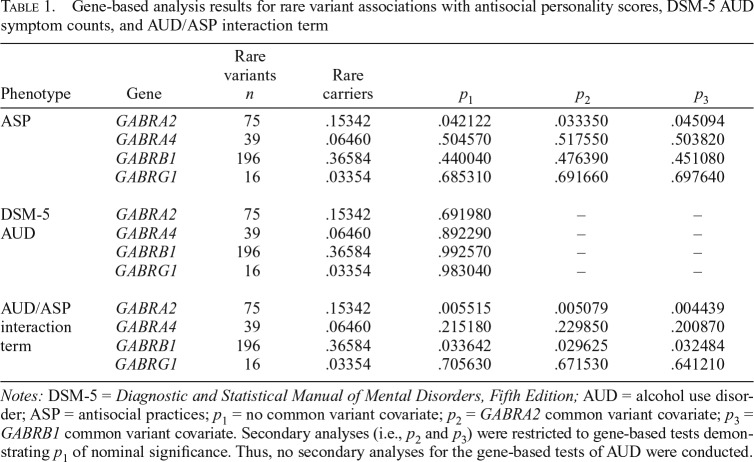
Table 1.
Gene-based analysis results for rare variant associations with antisocial personality scores, DSM-5 AUD symptom counts, and AUD/ASP interaction term
| Phenotype | Gene | Rare variants n | Rare carriers | p1 | p2 | p3 |
| ASP | GABRA2 | 75 | .15342 | .042122 | .033350 | .045094 |
| GABRA4 | 39 | .06460 | .504570 | .517550 | .503820 | |
| GABRB1 | 196 | .36584 | .440040 | .476390 | .451080 | |
| GABRG1 | 16 | .03354 | .685310 | .691660 | .697640 | |
| DSM-5 | GABRA2 | 75 | .15342 | .691980 | – | – |
| AUD | GABRA4 | 39 | .06460 | .892290 | – | – |
| GABRB1 | 196 | .36584 | .992570 | – | – | |
| GABRG1 | 16 | .03354 | .983040 | – | – | |
| AUD/ASP interaction term | GABRA2 | 75 | .15342 | .005515 | .005079 | .004439 |
| GABRA4 | 39 | .06460 | .215180 | .229850 | .200870 | |
| GABRB1 | 196 | .36584 | .033642 | .029625 | .032484 | |
| GABRG1 | 16 | .03354 | .705630 | .671530 | .641210 |
Notes: DSM-5 = Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition; AUD = alcohol use disorder; ASP = antisocial practices; p1 = no common variant covariate; p2 = GABRA2 common variant covariate; p3 = GABRB1 common variant covariate. Secondary analyses (i.e., p2 and p3) were restricted to gene-based tests demonstrating p1 of nominal significance. Thus, no secondary analyses for the gene-based tests of AUD were conducted.