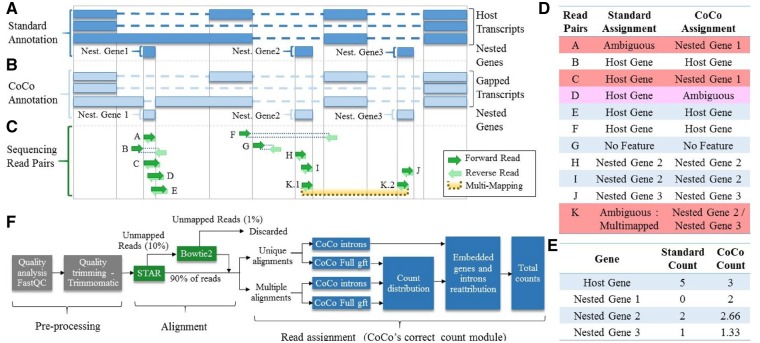
Fig. 1.
CoCo read correction scheme for nested and multimapped genes. (A) Representation of a standard gene annotation used for depicting a genetic locus containing one host gene and three nested genes. The dashed lines indicate introns while the dark blue boxes indicate exons. (B) Representation of the gene annotation produced using the correct_annotation module of CoCo showing a gap in the retained intron over the first nested gene. (C) Examples of potential read pairs overlapping the different features and multimapped read pairs. (D) Comparison of the read pair assignment using standard and CoCo pipelines, for each of the read pairs illustrated in (C). The reads that are differentially assigned by CoCo are highlighted in red. (E) Comparison of the read count estimates by the standard and the CoCo pipelines, based on the assignments listed in (D). (F) Flow chart of the CoCo pipeline. Pre-processing and alignment steps are shown before the correct_count module application. The correct_count module then assigns reads with Subread’s featureCounts using the gapped CoCo annotation (built with the correct_annotation module). Read pairs resulting in multiple alignments are considered separately and distributed proportionally to the uniquely assigned read pairs. (Color version of this figure is available at Bioinformatics online.)