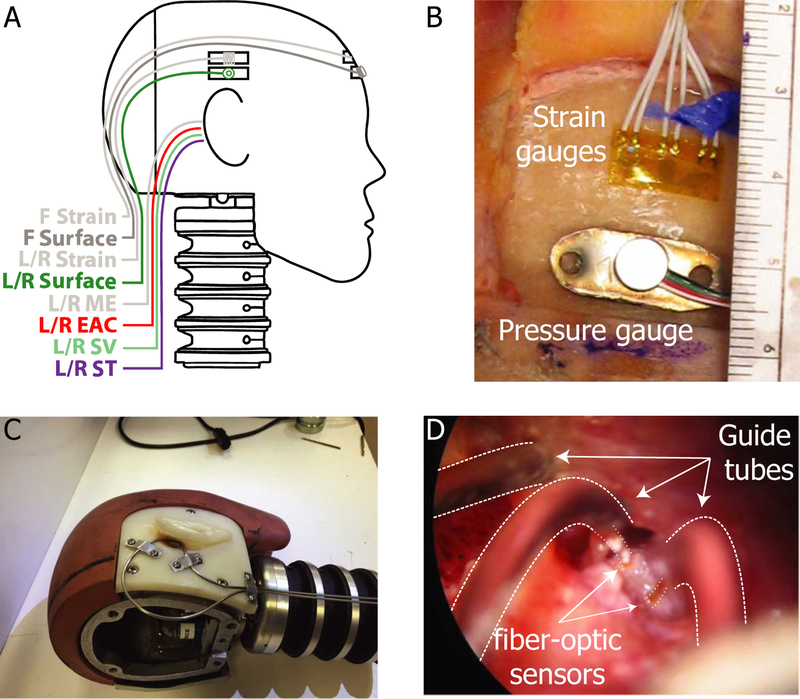
Fig. 1:
Locations and fixation methods for strain gauges and pressure sensors. A) Strain gauges and surface-mount pressure gauges were placed in three locations on the skull (Front/Left/Right). Fiber-optic pressure sensors (FOP-M) were placed into both ear canals (L/R EAC) and both middle ear (L/R ME) cavities. Fiber-optic pressure sensors (FOP-M260) were inserted bilaterally into the scala vestibuli (L/R SV) and scala tympani (L/R ST). B) Strain gauges and surface-mount pressure gauges were fixed to the surface of the skull in three locations with cyanoacrylate adhesive. C) Stainless steel tubing was securely mounted to the skull to guide and protect the fiber-optic pressure sensors (shown on a modified Hybrid III head). D) Fiber optic pressure sensors (bracketed by dotted lines) were inserted into the cochlea via small cochleostomies, sealed into the cochlea with alginate dental impression material, and fixed in place with cyanoacrylate adhesive along the length of the guide tube. Note, strain gauge responses are not presented in this report.