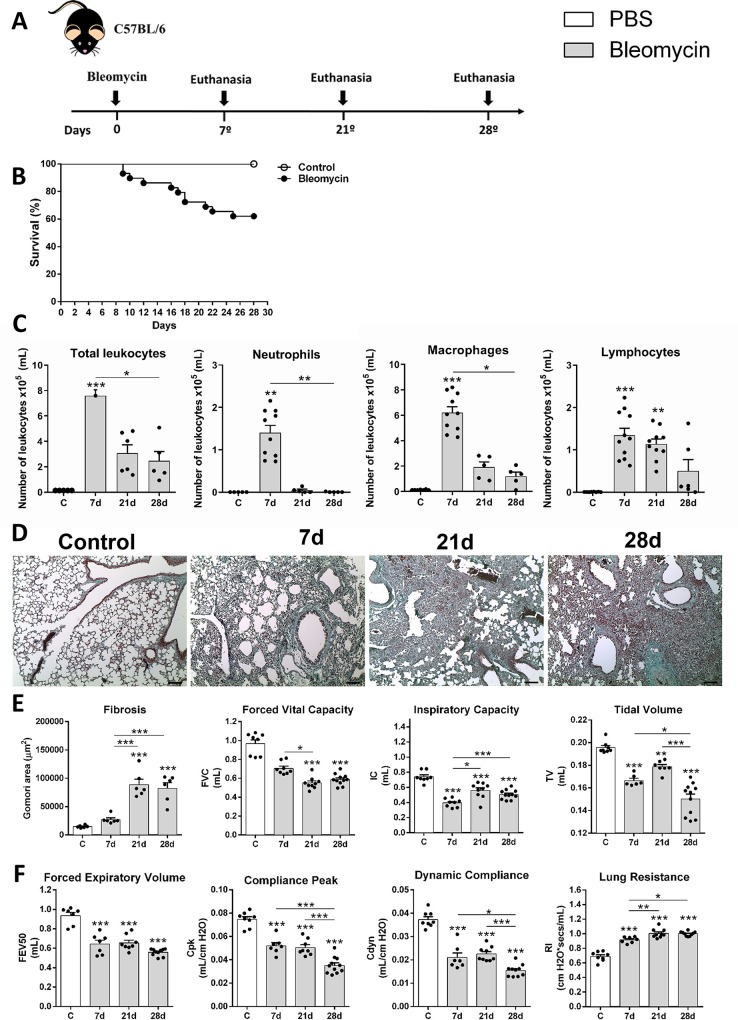
Fig 1. Characterization of Bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice.
(A) Experimental design of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (3 mg/Kg) in vivo in the times 7, 21 and 28 days after instillation of bleomycin; (B) Survival curves of mice treated with saline or bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis; (C) Quantification of total leukocytes in BAL, (D) differential counts of neutrophil, macrophage, and lymphocytes infiltration in BAL; (E) Gomori’s trichrome staining of lung sections in control and necropsied mice after 7, 21, 28 days after induction of fibrosis, Bar = 100μm; (F) Morphometric analysis of the fibrosis area. Measurement of pulmonary volumes (G): FVC, IC and TV; Analysis of airway flow by Forced Expiratory Volume at 50 milliseconds (FEV50) and lung elasticity by Cpk, Cdyn and Rl (H). Results represent mean ± S.E.M., *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001. One-way ANOVA test and Kruskal-Walis test followed by Dunn's test were used. Bar = 100μm.