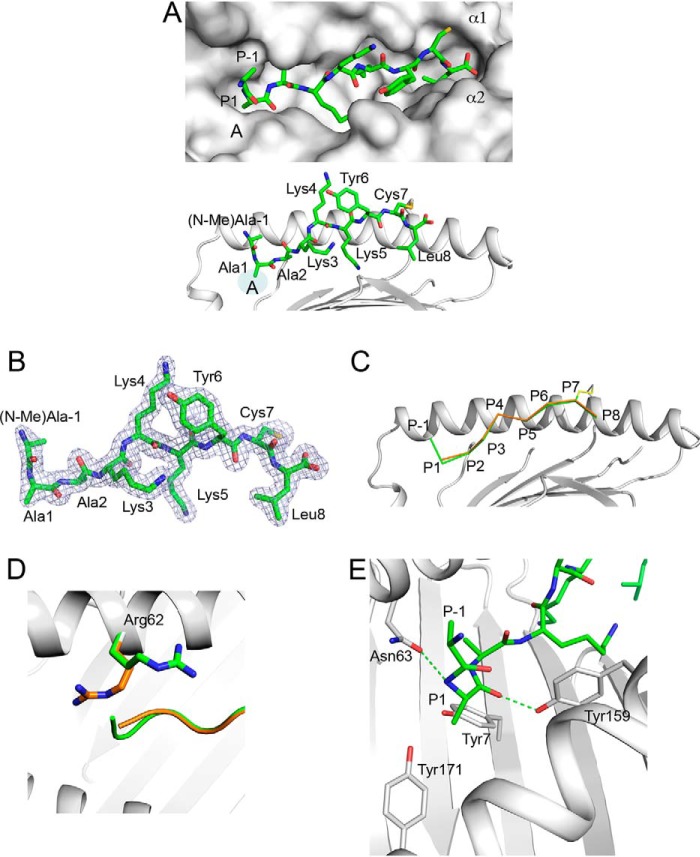
Figure 1.
Presentation of 10-mer (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL by HLA-B*0801E76C. A, top, molecular surface of HLA-B*0801E76C groove (light gray) showing the bound (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL (green) with P−1 (N-Me)Ala and P−2 Arg (see B) extending out of the A pocket. Peptide residue positions (P), A pocket, and α-helices are indicated. Bottom, bound conformation of (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL (green) shown against the α1-helix of HLA-B*0801E76C (light gray); the AAKKKYCL core binds into the groove, whereas P−1 (N-Me)Ala and P−2 Arg (see B) protrude out. The disulfide bond (yellow) between P7 Cys and Cys76 is shown. Peptide residues are labeled. B, 2mFo-DFc electron density, contoured at 1σ, is shown as blue mesh around (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL. The density is visible for all residues except for the N-methyl group of P−1 (N-Me)Ala and P−2 Arg. C, superimposition of the canonical structure of HLA-B*0801–bound GGKKKYKL (orange) (PDB entry 1AGD) with the structure of HLA-B*0801E76C–bound (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL (green), shown against the α1-helix of HLA-B*0801E76C (light gray). D, same as in C, showing that in the canonical structure of HLA-B*0801–bound GGKKKYKL (orange), Arg62 occupies a position that blocks the A pocket. In contrast, in the structure of HLA-B*0801E76C-bound (R(N-Me)A)AAKKKYCL (green), Arg62 has moved up and out, which opens the A pocket and allows the extensions to protrude out. E, details of interactions within the A pocket showing rotation of P1 Ala and its effect on P−1 (N-Me)Ala position. The H-bonds between the main-chain nitrogen of P1 Ala and Asn63 and between the main-chain carbonyl oxygen of P1 Ala and Tyr159 are shown as green dashed lines.