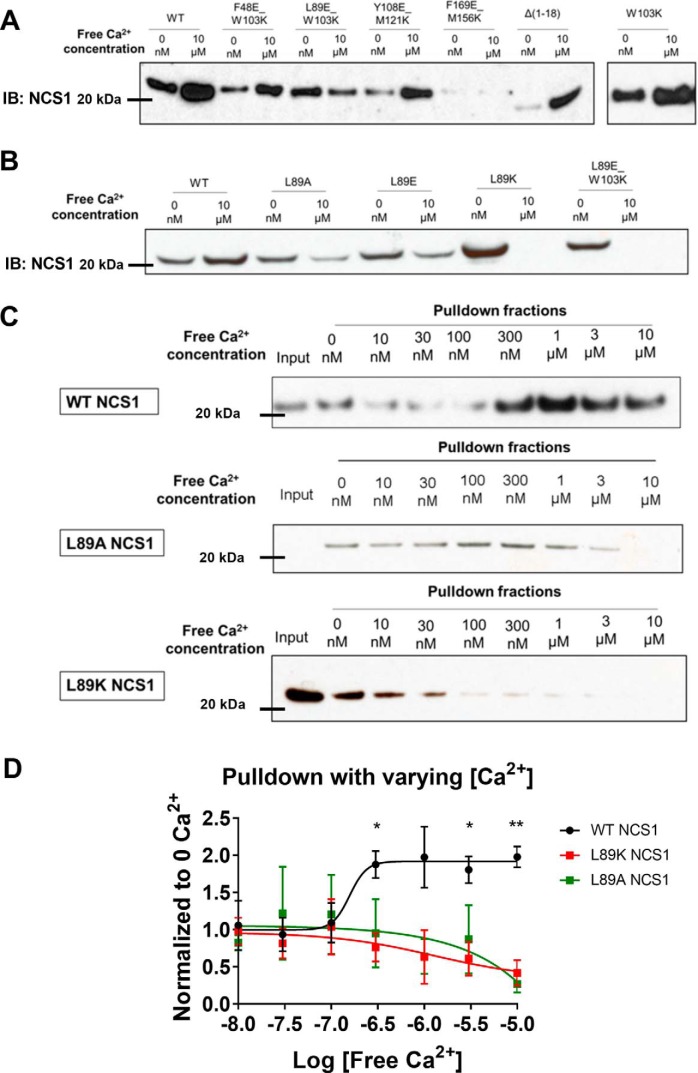
Figure 2.
The Leu-89 residue on NCS1 is important for the Ca2+-dependent NCS1–InsP3R1 interaction. A, GST-InsP3R1 (1–225) pulldown of WT and mutant NCS1 in Ca2+-free and Ca2+-containing conditions. Only the L89E/W103K mutant showed an inverted trend where Ca2+ reduced instead of increased interaction. B, mutation of the Leu-89 residue to Ala, Glu, or Lys all decreased the NCS1–InsP3R1 interaction in the presence of Ca2+. C, interaction between the WT and Leu-89 NCS1 variants over a range of physiologically relevant Ca2+ concentrations from 0 to 10 μm. D, quantification of four experiments for WT NCS1 (same data as shown in Fig. 1E), four experiments for L89K, and three experiments for L89A. *, statistically significant difference between WT NCS1 and Leu-89 NCS1 variants at that specific Ca2+ concentration (Student's t test, adjusted for multiple comparison). Fit show was from log(agonist) versus response. Error bars show S.E. IB, immunoblotting.