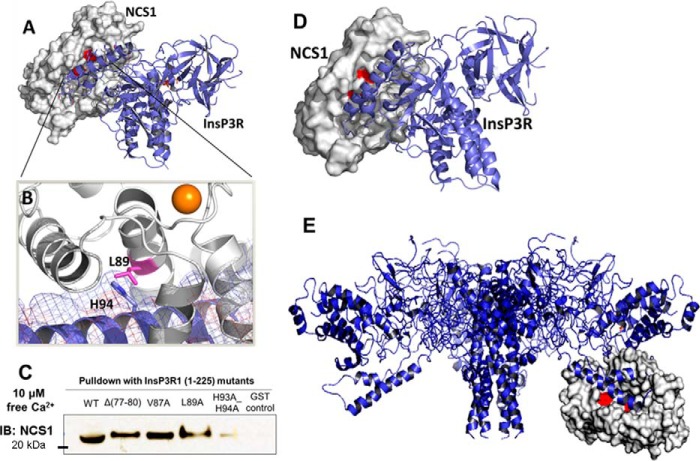
Figure 3.
A, prediction of the molecular interaction between Ca2+-bound NCS1 (white, PDB code 1G8I) and a fragment of InsP3R1 (blue) containing residues 1–604 (PDB code 3UJ0) using the ZDOCK server. B, Leu-89 (shown in pink) of NCS1 forms interactions with the arm motif of the suppressor domain of InsP3R1 (residues 66–110). Mutations L89A, L89E, and L89K would likely disrupt binding to this region of the InsP3R. C, mutation of His-93/His-94 to Ala reduced NCS1–InsP3R1 interaction in the presence of Ca2+ D, a nearly identical binding geometry for complex formation between NCS1 and InsP3R1 was predicted by the ClusPro server using an independent docking algorithm. E, visualization of NCS1 binding to full-length InsP3R. Molecular interactions between NCS1 (white, PDB code 1G8I) and a fragment of InsP3R1 (blue) containing residues 1–604 (PDB code 3UJ0) were predicted using the ZDOCK server and superimposed in PyMOL on the structure of full-length InsP3R1. The predicted binding site is in the cytoplasmic domain and appears accessible by NCS1. IB, immunoblotting.