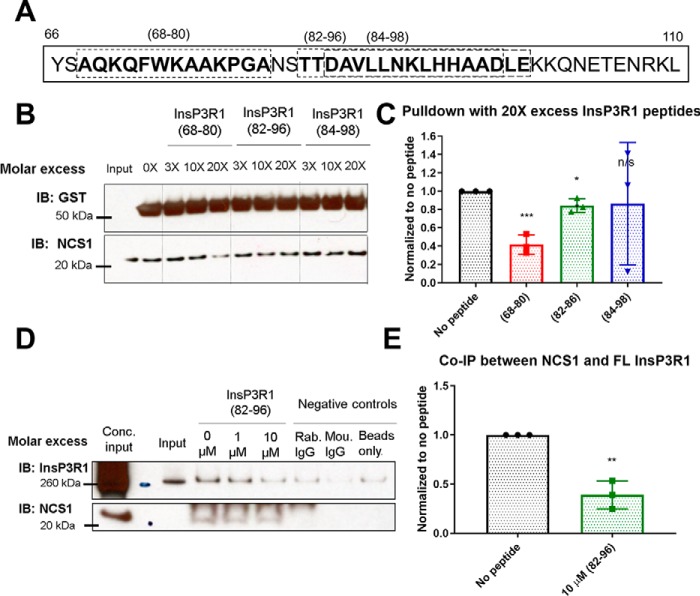
Figure 4.
InsP3R1 peptides corresponding to NCS1 binding region reduced NCS1-InsP3R1 interaction. A, diagram showing the InsP3R1 peptides tested within the predicted binding region spanning residues 66–110, with the peptides used shown in boxes. B, representative blot of pulldown between GST-InsP3R1 (1–225) and NCS1 in the presence of various concentrations of peptides and 10 μm Ca2+. C, quantification of 3 independent experiments with peptides added at 20X molar excess (2 μm peptide, 100 nm NCS1). Addition of peptides (68–80) and (82–96) resulted in a 58% (p = .0007) and 16% reduction (p = 0.02) in the amount of NCS1 pulled down respectively, whereas addition of peptide (84–98) did not change the amount of NCS1 pulldown (p = 0.09) (two-tailed student t-test comparing the no peptide control with the specific peptide). D, representative blot of co-immunoprecipitation between NCS1 and full-length InsP3R1 with blocking peptides. E, peptide (82–96) also reduced the interaction between NCS1 and full-length InsP3R1 by 60% in mouse cerebellum lysate (n = 3, two-tailed student t-test, p = 0.002).