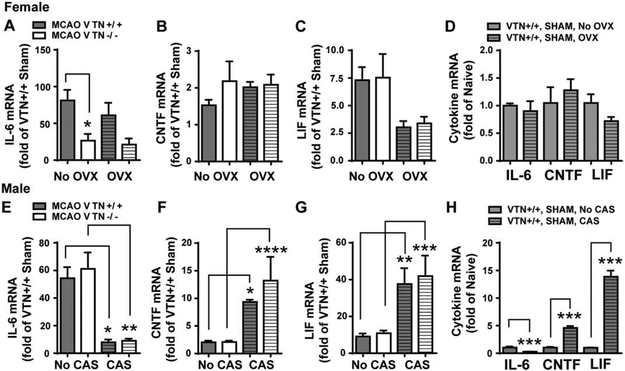
Figure 4. Only VTN−/− females have lower IL-6 following MCAO but in a gonadal hormone-independent manner.
Female and male VTN+/+ and VTN−/− mice were ovariectomized (OVX) or castrated (CAS), respectively. Two weeks later, they received a sham operation or a 30 min MCAO. After 24 h, the cytokine mRNA in the SVZ were measured by RT-qPCR and expressed as a fold change compared to VTN+/+ shams within each sex. A) In female mice without OVX (first two columns), MCAO-induced IL-6 was substantially lower in VTN−/− mice compared to VTN+/+ mice, indicating that VTN induces IL-6 following MCAO in female mice. The MCAO-induced CNTF (B) and LIF (C) were comparable between VTN+/+ and VTN−/− females. After OVX, the lower MCAO-induced increase in IL-6 of VTN−/− females (A) was not different from the lower levels seen in VTN−/− females without OVX, suggesting that ovary hormones do not contribute to VTN-induced IL-6 following MCAO. Levels of CNTF (B) and LIF (C) were also similar between VTN+/+ and VTN−/− females after OVX alone. OVX itself did not significantly alter IL-6, CNTF and LIF mRNA in MCAO sham-operated mice compared to no OVX (D). In males without CAS (first two columns) and with CAS (the last two columns), MCAO-induced IL-6 (E), CNTF (F) and LIF (G) were comparable between VTN+/+ and VTN−/− mice, suggesting that male sex hormones do not affect the VTN regulation of these cytokines following MCAO. However, CAS substantially reduced IL-6 (E) and increased CNTF (F) and LIF (G) following MCAO. H) CAS-induced changes in these cytokines were also observed in MCAO sham-operated mice. N = 7, 6, 9 and 10 in female mice and 10, 12, 4 and 5 in male mice for MCAO. N= 4 and 5 mice in female sham, N = 3 and 5 mice in male sham. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001 (Two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey multiple comparisons).