Figure 3 – Object sequence task.
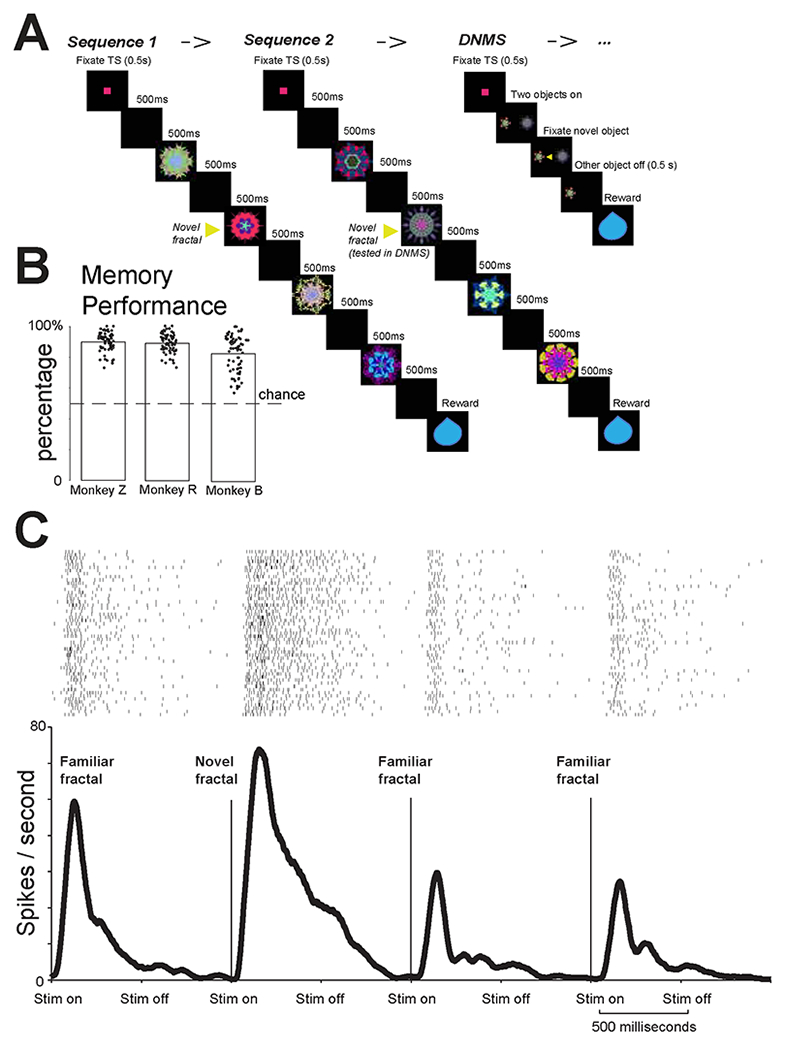
(A) The monkey was first shown two sequences of fractals. Each sequence contained 4 fractals, in which 1st, 3rd, 4th fractals were fixed familiar objects and 2nd fractal was always novel. After the two sequences, the monkeys performed a delayed non-match to sample task (DNMS) in which one object was novel and the other was the object that was previously novel in sequence 2. Monkeys fixated the novel object for reward. (B) Behavioral performance for three monkeys. Y-axis shows the percentage of first saccades to the novel object in DNMS, the percentages are significantly different from 0.5 for all three monkeys (p<0.01, sign-rank test). (C) Example BF phasic bursting neuron’s responses to the four objects in in a sequence. The response was highest for the second (novel) fractal (rank sum test; p<0.05).
