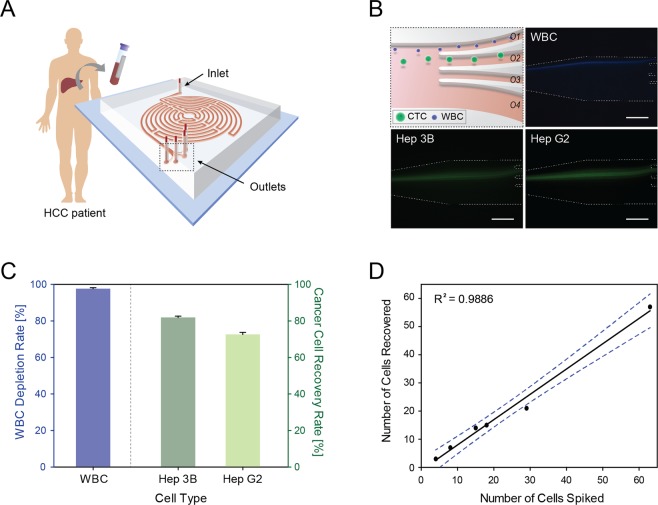
Figure 1.
Characterization of the Labyrinth device with HCC cell lines. (A) CTC isolation workflow using the Labyrinth device. Red blood cells (RBCs) were removed from whole blood, sampled from HCC patients using density gradient separation prior to device injection. (B) CTC separation from white blood cells (WBCs) by differential inertial focusing and collection. Fluorescent microscope image of differentially focused cell streaks by inertial focusing and migration for cell separation. CTCs were collected through outlet 2 (O2). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (C) HCC cell line recovery and WBC depletion rate of the Labyrinth. Labyrinth operated at a constant flow rate of 2000 μl/min. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicates. (D) CTC isolation performance. Small aliquots of HCC cells (5–100 Hep 3B cells) were spiked into whole non-HCC subject (control) blood and subjected to Labyrinth recovery.