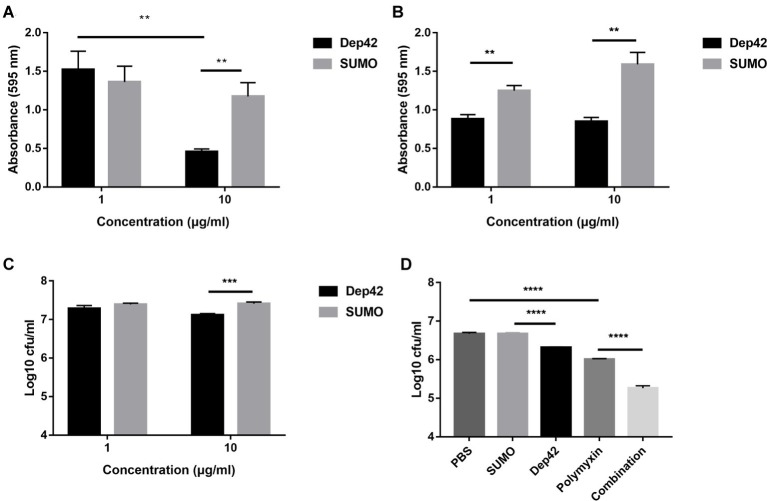
Figure 7.
Antibiofilm and antibacterial activity of Dep42. (A) Dep42 inhibited the formation of biofilms. Dep42 or SUMO at 1 and 10 μg/ml was incubated with K. pneumoniae 2226 in 96-well plates for 48 h. The residual biofilm was assessed by crystal violet staining, and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm. (B,C) Dep42 disrupted the mature biofilm. Biofilm formation of K. pneumoniae strain 2226 was induced in 96-well plates for 48 h, and then, the biofilm was treated with depolymerase (black bar) or SUMO (gray bars) at 1 and 10 μg/ml for 3 h. The residual biofilm was assessed by crystal violet staining (B) and viable cell counting (C). (D) Dep42 enhanced the antimicrobial activity of polymyxin. Biofilm formation of K. pneumoniae strain 2226 was induced in 96-well plates for 48 h, and then, the biofilm was treated with Dep42 (10 μg/ml), polymyxin (6 μg/ml), or Dep42 (10 μg/ml) followed by polymyxin (6 μg/ml) as indicated. The treatment groups with PBS and SUMO (10 μg/ml) were included as negative controls. The viable bacterial count was determined on LB agar plates. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM; * indicates p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.