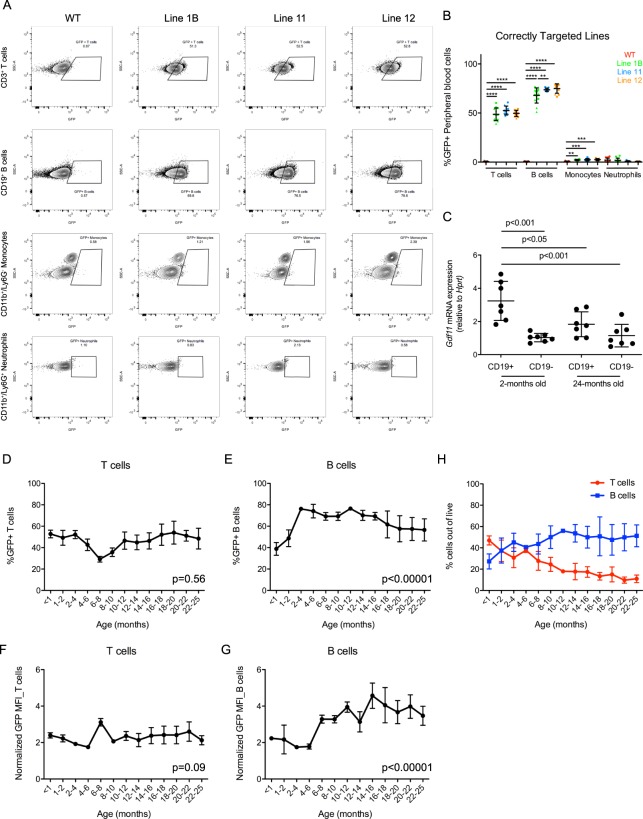
Figure 3.
Gdf11-IRES-GFP expression is primarily detected within T and B lymphocytes of the peripheral blood. (A) Representative flow cytometry analysis of GFP expression within CD3+ T cells, CD19+ B cells, CD11b+/Ly6G− monocytes and CD11b+/Ly6G+ neutrophils from peripheral blood. (B) Quantification of GFP+ T cells, B cells, monocytes and neutrophils in 2 month old mice from lines 1B, 11 and 12 and WT controls. N = 3–8 males and 3–8 females per genotype. Circles: males. Triangles: Females. Individual data points overlaid with mean ± SD. (C) Real time PCR analysis of Gdf11 levels in CD19+ and CD19- splenic cells from young (2-month old) and aged (24-month old) mice. Hprt was used as a housekeeping gene. (D,E) Quantification of (D), GFP + peripheral blood T cells and (E), GFP + peripheral blood B cells within heterozygous mice from line 1B during aging. (F,G) Quantification of GFP mean fluorescence intensity within F, peripheral blood T cells and (G), peripheral blood B cells in heterozygous mice from line 1B during aging. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values normalized to wild type mice for each timepoint. (H) Quantification of total T cell frequency (red) and B cell frequency (blue) out of live peripheral blood cells during aging. N = 25 males and 19 females. Data points represent mean with error bars denoting SEM.