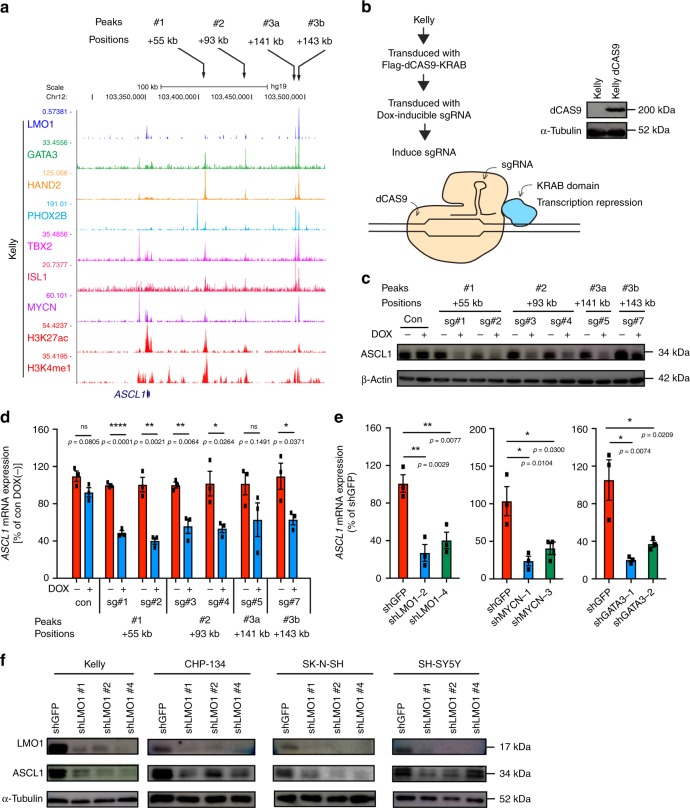
Fig. 4.
ASCL is directly regulated by LMO1 and MYCN in neuroblastoma cells. a ChIP-seq gene tracks showing the binding locations of various transcription factors at the ASCL1 gene locus in Kelly cells. Black arrows (top) indicate regions associated with H3K27ac signals in Kelly cells (peaks 1, 2, 3a, and 3b). b Kelly cells was first transduced with the dCas9-KRAB protein. sgRNAs (sg#1–7) targeting each of peaks bound by LMO1 (peaks 1, 2, 3a and 3b) were then induced by the treatment with doxycycline (DOX) (right). Protein expression of dCas9 was confirmed by western blot (left). α-tubulin was used as an internal control. c Protein expression of ASCL1 after the induction of each sgRNA was analyzed by western blot. d mRNA expression of ASCL1 after the induction of each sgRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Expression was normalized to spike-in control RNA and shown as a percent relative to untreated control samples. Data are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) for three biological replicates. The p values by two-tailed unpaired t test are indicated. e mRNA expression of ASCL1 after knockdown of LMO1, MYCN, and GATA3 in Kelly cells were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Expression was normalized to spike-in control RNA and shown as a percent relative to control shGFP. Data are represented as means ± SEM for three biological replicates. The p value by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons post hoc test are indicated. f Protein expression of LMO1 and ASCL1 were analyzed after transduction of different LMO1 shRNAs in five different neuroblastoma cell lines.