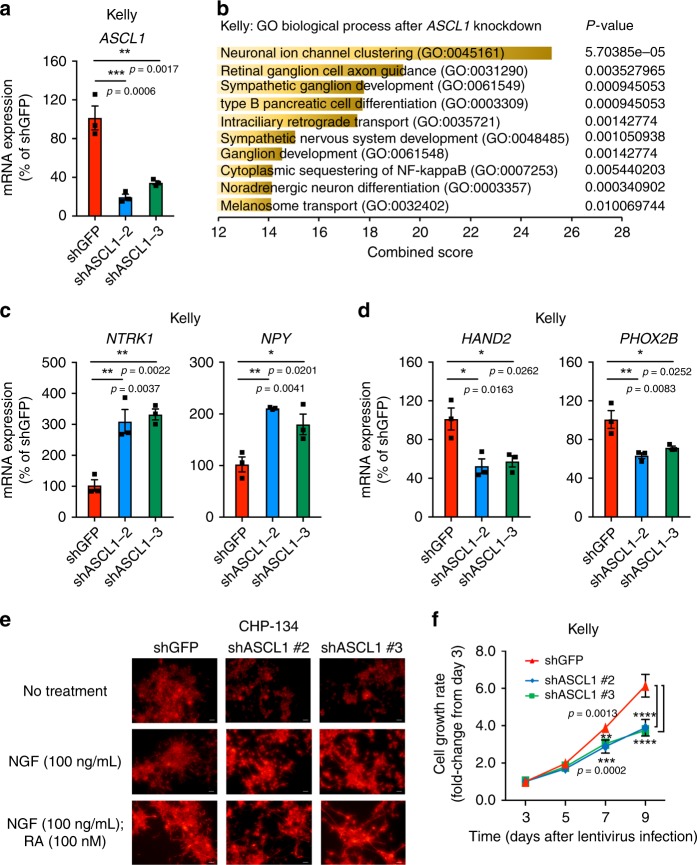
Fig. 7.
ASCL1 is required for cell growth and regulates neural differentiation status. a Two different shRNAs targeting ASCL1 (#2, 3) were transduced into Kelly cells. The mRNA expression of ASCL1 was measured by qRT-PCR, and shown as a percent relative control shGFP. Data are represented as means ± SEM for three biological replicates. The p value by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons post hoc test are indicated in a, c, d, and f. ****p value < 0.0001. b The shRNA targeting ASCL1 or control (GFP) was transduced into Kelly by lentiviral infection. Experiments were done in biological duplicates. Total RNAs were harvested after 3 days of infection and were subjected to RNA-seq analysis to compare gene expression profiles between two controls and two ASCL1 knockdown (KD) samples. Genes differentially expressed (adjusted p value < 0.05, log2 fold-change <−0.5 and TPM > 3) were selected for gene ontology analysis. Top ten terms were shown with combined score. The p values by the Fisher exact test are indicated. c, d The mRNA expression of genes involved in neural differentiation and mRNA expression of CRC members were analyzed by qRT-PCR after ASCL1 knockdown in Kelly cells. Expression was shown as a percent relative to shGFP control. Data are represented as means ± SEM for three biological replicates. e CHP-134 cells were treated with or without NGF (100 ng/mL) or/and ATRA (100 nM) after being transduced with shRNAs. The cells were then stained with an antineurofilament antibody, with images representative of three fields taken at ×40 original magnification. Scale bars were shown in white at bottom right, 20 μm. f Cell viability was measured after 3, 5, 7, and 9 days of infection in Kelly cells (n = 3 per group). The growth rate (fold-change) over 9 days compared with day 3 was indicated. Values represent means ± SD for technical triplicates.