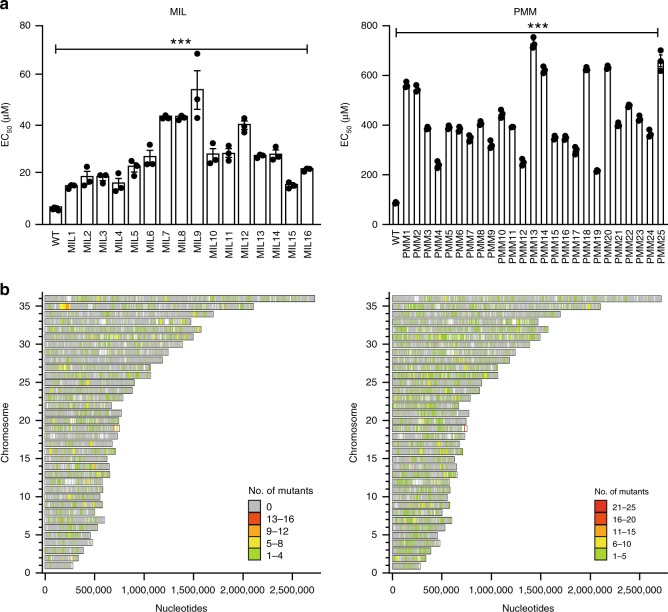
Fig. 1. Drug susceptibility and mutations in Leishmania selected for resistance.
a Susceptibility to miltefosine (MIL; left panel) and paromomycin (PMM; right panel) were performed on individual clones. The wild-type L. infantum (WT) is shown for both drugs. The MIL resistant mutants were selected after mutagenesis with either EMS or HMPA (Supplementary Table 1) while the PMM-resistant mutants were selected after mutagenesis with EMS, ENU, or MMS (Supplementary Table 1). Data are mean ± SEM. For the MIL susceptibility assay, n = 5 biologically independent replicates for the wild-type and n = 3 biologically independent replicates for the mutants. For the PMM susceptibility assay, n = 3 biologically independent replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired two-tailed t-tests. ***P < 0.001. b Genome-wide distribution of SNVs in mutants selected against MIL (left panel) and PMM (right panel). Bars represent the genes on each chromosome. Colored bars represent genes mutated in defined numbers of mutant clones; gray bars represent non-mutated genes. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.