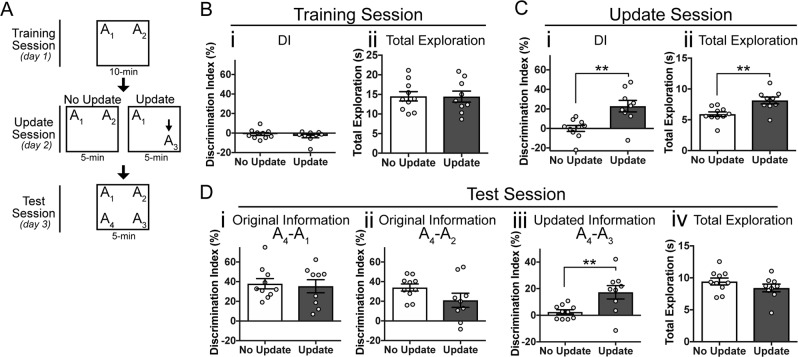
Fig. 1.
Young mice successfully perform memory updating in the OUL task. a Experimental design. b Training session behavior. Mice show a low DI, indicating no preference for object A1 or A2 (left) and have similar levels of total object exploration (right). c Update session behavior. (i) Mice in the Update condition prefer the novel location A3 to the familiar location A1 whereas No Update mice show similar exploration of the familiar locations A1 and A2, with a DI near zero. (ii) Update mice show significantly more total object exploration than No Update mice. d Behavior during the test session. (i) Mice in both the Update and No Update group show intact memory for the original training object location A1. (ii) Both groups also show memory for original training location A2. (iii) Only the Update group shows a preference for the novel location A4 over the updated location A3; No Update mice prefer objects A3 and A4 equally. (iv) Mice show similar levels of total object exploration during the test session. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01