Figure 1.
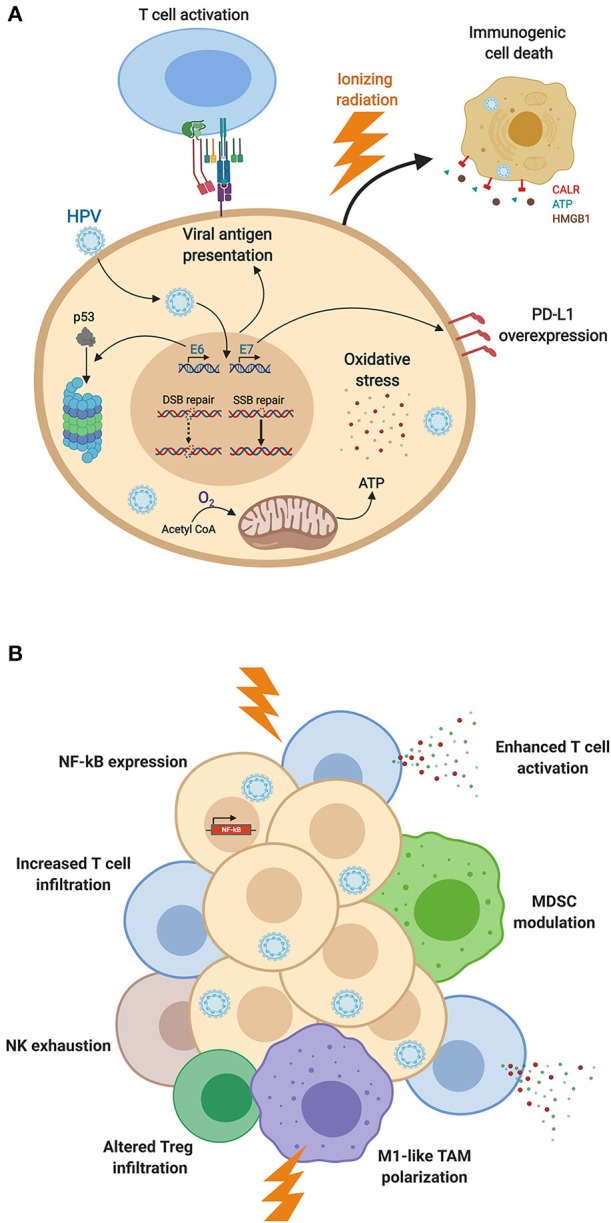
HPV-induced modifications of (A) cancer cell biology and (B) immune responses, impacting the radiation response. (A) Expression of HPV-associated proteins induces adaptations of cellular biology, including DNA repair dysfunction, proteasomal degradation of p53 altering cell cycle distribution, E7-induced PD-L1 expression, HPV-mediated oxidative stress, and viral antigen presentation. These cellular modifications as well as mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation enhance cancer cell sensitivity to ionizing radiation and promote immunogenic cell death. (B) HPV-mediated NF-kB activation, T cell infiltration and activation, and M1-like TAM polarization are enhanced by radiation, promoting anti-cancer immunity after irradiation of HPV-driven HNSCC. HPV-associated MDSC modulation as well as NK cell exhaustion offer additional therapeutic targets to boost anti-tumor responses (Figure created with BioRender.com).
