Figure 1.
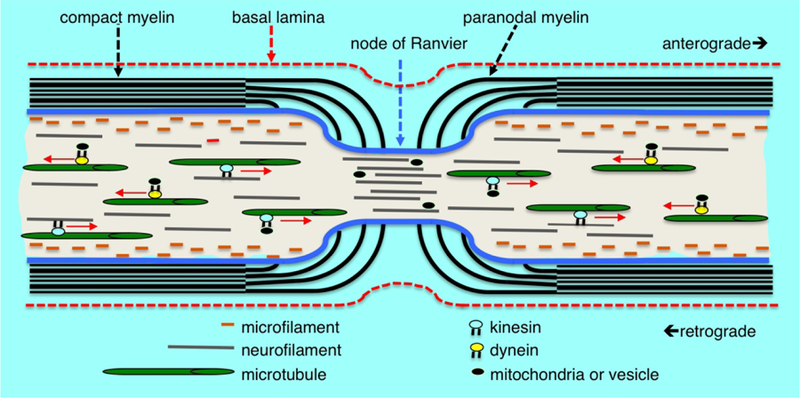
Myelin structure, cytoskeleton arrangement and axonal transport at the node of Ranvier. Microfilaments of polymeric actin align along the axolemma, neurofilaments are distributed throughout the axoplasm and microtubules are arranged more centrally in the axoplasm. Cytoskeletal components, vesicles and mitochondria are transported anterograde and retrograde along microtubule tracts by the mechano-chemical motors kinesin and dynein, respectively. Compact myelin opens into cytoplasmic loops in the paranodal region with microvilli projections contacting the axolemma. There is a rapid decrease in the axonal diameter at the node of Ranvier accompanied by an increased density of neurofilaments having a decreased state of phosphorylation. There is also an increased density of vesicles and other organelles within the axon at the node suggesting an impediment to transport at the nodal constriction.
