Figure 3.
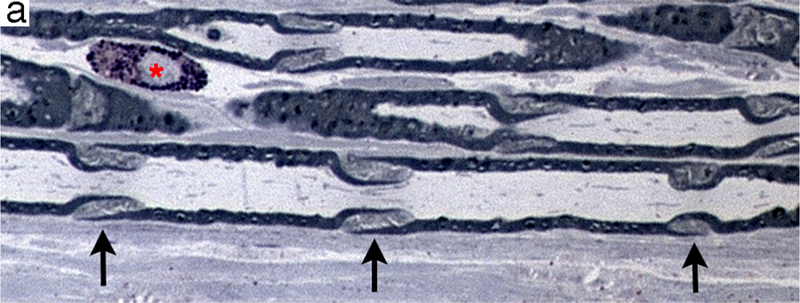

Regions of non-compact myelin that are affected earliest during axonal degeneration. (a) Longitudinal section of plastic-embedded toluidine blue-stained rat sciatic nerve showing Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (arrows) distributed along the internode. These structures consist of non-compact myelin that provide a cytoplasmic pathway connecting the Schwann cell cytoplasm adjacent to the axon to that on the external myelin sheath. A mast cell (*) is present in the endoneurium. (b) Transverse section through the paranodal region of a large myelinated fiber. The axon (ax) is constricted and contains a high density of neuroflaments and organelles. The compact myelin has opened to form folded myelin (fm) and microvilli (mv) that contact the axolemma.
