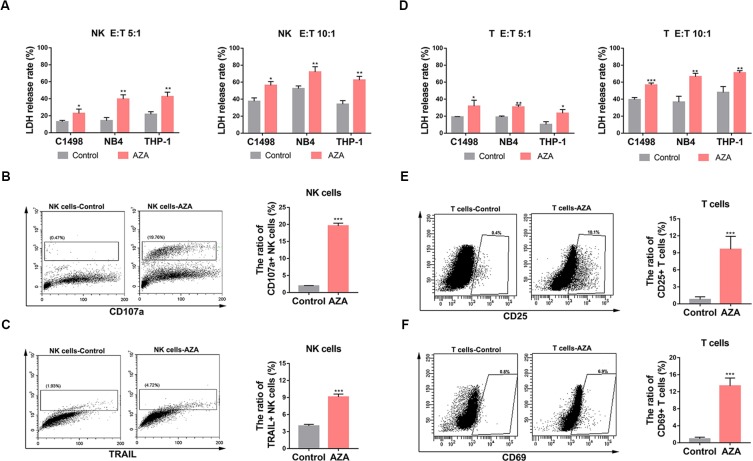
Figure 3.
Azelaic acid (AZA) promotes the activation of NK and T cells and enhances cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. (A, D) NK and T cells were treated with 10 µM AZA for 48 h before incubation with AML cell lines at different E:T ratio for the cytotoxicity assay (E:T = 5:1 and 10:1). Cytotoxicity was measured by an LDH assay. (B, C) NK cells were treated with 10 µM AZA for 48 h before incubation with the AML cell lines at an E:T ratio of 3:1. Cells were then stained with CD107a and TRAIL for flow cytometric analysis. Right, the percentage of positive staining cells. (E, F) T cells were treated with 10 µM AZA for 48 h before incubation with the AML cell lines at an E:T ratio of 3:1. Cells were then stained with CD25 and CD69 for flow cytometric analysis. Right, the percentage of positive staining cells. A total of three independent experiments were performed, diagrams represents mean percentage, statistical significance was determined with student's test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.