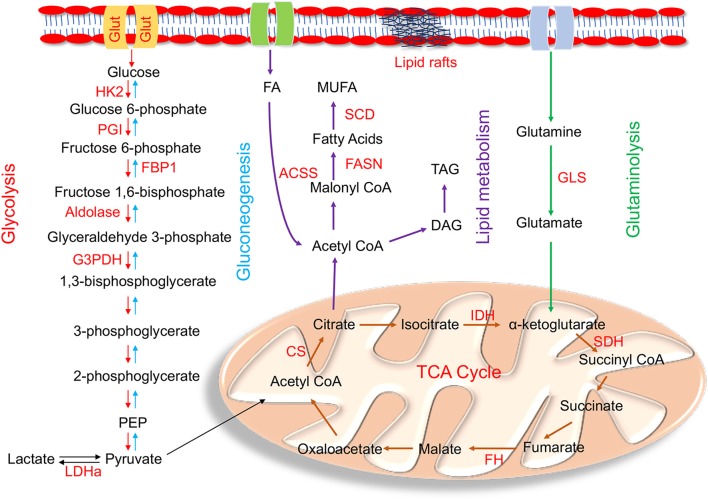
Figure 1.
Enzymes within their pathways that are implicated in metabolic reprogramming during EMT. Schematic diagram of enzymes (highlighted in red) within the metabolic pathways of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, mitochondrial, glutamine, and lipid metabolism alluded in the text that are altered during metabolic reprogramming that occurs in EMT. The main glycolytic enzymes that are upregulated in EMT are HK2 (hexokinase 2); PGI (phosphoglucoisomerase); aldolase, G3PDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase), and LDHa (lactate dehydrogenase a). FBP1 (fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase), the rate limiting enzyme of gluconeogenesis, is downregulated during EMT. Mutations in the tri-carboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzymes linked to EMT are IDH (isocitrate dehydrogenase); SDH (succinate dehydrogenase); FH (fumarate hydratase); and CS (citrate synthase). The key enzyme involved in glutaminolysis is GLS (Glutaminase). De novo lipogenesis key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism are ACSS (acyl CoA synthetase); FASN (fatty acid synthase); and SCD (stearoyl CoA desaturase). Cells undergoing EMT also have high TAG (Triacylglycerols) levels.