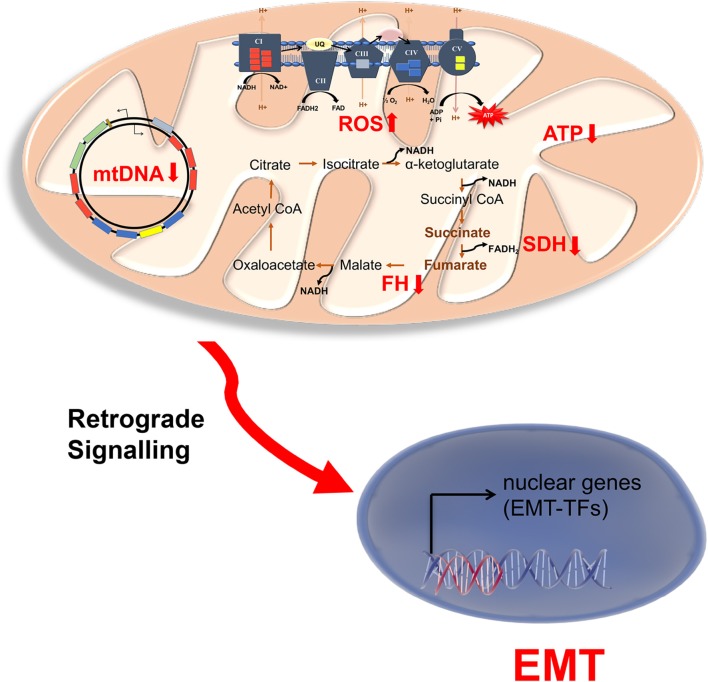
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in endocrine cancers. Schematic representation of mitochondrial disruptions associated with EMT in endocrine cancers. NADH and FADH2 produced in the TCA cycle is utilized by electron transport chain (ETC) to produce ATP for Oxphos. As mitochondrial encoded genes are limiting for Oxphos, mutation in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) also causes low mitochondrial ATP and increased ROS (reactive oxygen species) production. The increase production of ROS and/or mutation in the TCA cycle enzymes succinate dehydrogenase (SCD) and fumarate hydratase (FH) result in accumulation of succinate and fumarate. These might be involved in retrograde signaling to activate nuclear EMT transcription factors, particularly in neuroendocrine cancers pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma.